In the world of stainless steel, three types of grades, 303, 304, and 316, have attracted a lot of attention due to their unique properties and applications. So, what’s the difference between 303 vs 304 vs 316 stainless steel? In fact, the differences between them not only lie in their basic chemical composition, but also involve their corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and compatibility with other materials in different environments. This article will explore the characteristics of these three stainless steels in depth to help you understand their respective advantages and applicable scenarios so that you can make informed decisions when choosing the right stainless steel material.

303 vs 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel: What’s the Difference?
303 vs 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel – 1. Price:
In fact, the most intuitive aspect is the price of 303, 304, and 316 stainless steel, which are not the same. Generally speaking, the price of 316 stainless steel is the highest because it contains the valuable element molybdenum. The price of 304 stainless steel is second, as it is the most commonly used type of stainless steel. The price of 303 stainless steel is the lowest because it contains the harmful element sulfur. The specific price varies according to market supply and demand and material specifications, and cannot be generalized.
303 vs 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel – 2. Compositions:
Secondly, there are differences in composition. The compositions of 303, 304, and 316 stainless steel are as follows:
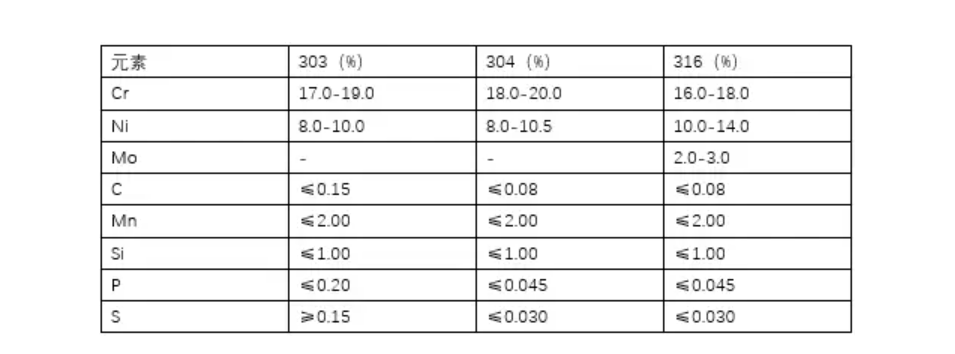
As can be seen from the table, 303 stainless steel has more carbon, sulfur, and phosphorus than 304 and 316 stainless steel, but less chromium and nickel. These differences mainly affect their strength and processability. Carbon can make stainless steel harder and stronger, but it can also make it brittle and brittle, and it is prone to rusting at high temperatures or during welding.
Sulfur and phosphorus are impurity elements that can make stainless steel easy to cut and process, but also make it less corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant. Chromium and nickel are good elements that can make stainless steel corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant, as well as having good softness and toughness. Molybdenum is also a good element that can make stainless steel more corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant, especially for media such as chlorides, sulfates, and phosphates.
303 vs 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel – 3. Corrosion Resistance
In terms of corrosion resistance, 303, 304, and 316 stainless steels are all relatively resistant to corrosion, especially for weak corrosive media such as air, water, acetic acid, and citric acid. They are much better than ordinary steel and low alloy steel. This is mainly due to the chromium element in them, which can form a protective film on the surface of stainless steel to protect the steel from rusting. Therefore, 303, 304, and 316 stainless steels are suitable for various structural components and parts in the engineering construction industry, such as building exterior walls, bridge load-bearing, pipeline transportation, mechanical equipment, furniture decoration, etc.
However, 316 stainless steel has stronger corrosion resistance, especially for strong corrosive media such as chlorides, sulfates, and phosphates, which is much better than 303 and 304 stainless steel. This is because 316 stainless steel contains molybdenum, which can form a more stable protective film to protect the steel from strong corrosive media. Therefore, 316 stainless steel is suitable for use in some special environments in the engineering construction industry, such as production equipment for seawater, chemicals, dyes, paper, oxalic acid, fertilizers, and other industries, as well as photographic and food industries, coastal facilities, etc.
303 vs 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel – 4. Strength
The engineering strength of 303, 304, and 316 stainless steels is relatively soft and ductile, but their strength is not low. Their yield strength is around 200 MPa and tensile strength is around 500 MPa. These strengths can be improved through cold processing, but not through heat treatment. Cold processing can make stainless steel harder and stronger, but it can also make it thinner and more magnetic. Heat treatment can make stainless steel softer and thinner, but it can also make it thinner and rusty.
303 vs 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel – 5. Heat Resistance
Heat resistance: 303, 304, and 316 stainless steels are all relatively heat-resistant, but 316 stainless steel is more heat-resistant. They can all be used at temperatures below 1600 degrees Celsius, and can also be used in the range of 800-1575 degrees Celsius, but it is best not to use them for a long time. If you use 316L stainless steel (L represents low carbon), then you can use it for a long time in this temperature range and it can also resist intergranular rusting. Intergranular rusting is a phenomenon where carbon elements gather at grain boundaries during high temperatures or welding to form carbides, resulting in rusting.
303 vs 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel – 6. Welding
In welding operations, 303, 304, and 316 stainless steels are relatively easy to weld, but 303 stainless steel has poor weldability due to its high sulfur content. They can all be welded using all standard welding methods. During welding, corresponding filler materials can be used depending on the application.
Conclusion
In the engineering construction industry, the choice of stainless steel depends on specific applications and environments. Generally speaking, if high corrosion resistance and heat resistance are required, 316 stainless steel can be selected; if high machinability is required, 303 stainless steel can be selected; if both performance and price are required, 304 stainless steel can be selected.
Thank you for reading our article and we hope it can help you to have a better understanding of the differences between 303 vs 304 vs 316 stainless steel. If you want to learn more about stainless steel, we would advise you to visit Sino Stainless Steel for more information.
As a leading supplier of stainless steel products across the world, Sino Stainless Steel provides customers with high-quality stainless steel strips, stainless steel coils, stainless steel plates, stainless steel sheets, stainless steel bars, and stainless steel tubes at an extremely competitive price.
 :+86-13012867759
:+86-13012867759  :export86@sino-stainless-steel.com
:export86@sino-stainless-steel.com
buy priligy online safe Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes