Stainless Steel Suppliers
How to cut stainless steel?
Once upon a time, there was a talented metalworker named Alex. Known for their exceptional craftsmanship, Alex was sought after by many for their ability to shape stainless steel into stunning works of art. However, their secret weapon was their mastery of cutting techniques. One day, a group of aspiring metalworkers approached Alex, eager to learn the art of cutting stainless steel.
So how to cut stainless steel?
To cut stainless steel, we can use various methods. One common approach is using a power tool such as an angle grinder with a cutting disc specifically designed for stainless steel. Another option is using a plasma cutter or a laser cutter for more precise cuts. It’s essential to wear safety gear, secure the material, and choose the appropriate cutting tool for the desired outcome.
In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of stainless steel cutting, uncovering the techniques, tools, and tips that will empower you to cut stainless steel with precision and finesse. Join us on this journey to unlock the secrets of mastering the art of cutting stainless steel.
Table of Contents
I. Introduction
Cutting stainless steel is a crucial skill in various industries, from construction to manufacturing. As one of the most versatile and widely used materials, stainless steel offers exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. However, its unique properties present challenges when it comes to cutting. In this blog, we will explore the importance of stainless steel cutting, the challenges involved, and provide valuable insights on how to cut stainless steel effectively.

A. Explanation of the importance of stainless steel cutting
Stainless steel is extensively utilized in many applications due to its remarkable qualities. Its resistance to corrosion, heat, and chemical damage makes it an ideal choice for constructing buildings, manufacturing equipment, and creating household items.
To utilize stainless steel effectively, it often needs to be cut into specific shapes and sizes to fit various requirements. Proper cutting techniques are essential to achieve precise results, maintain structural integrity, and maximize the material’s potential.
B. Overview of the challenges and considerations involved in cutting stainless steel
While stainless steel is an excellent material, it poses unique challenges during the cutting process. Its high strength and hardness can make it difficult to cut using conventional tools. The risk of work hardening, heat buildup, and distortion is significant.
Additionally, the potential for tool wear and damage is higher compared to other metals. Therefore, understanding the intricacies of stainless steel cutting is vital to ensure efficient production, minimize waste, and maintain the quality of the finished products.
The purpose of this blog is to provide comprehensive guidance on how to cut stainless steel effectively. We will delve into various techniques, tools, and best practices that stainless steel suppliers and fabricators can employ to overcome the challenges associated with cutting this remarkable material. By the end of this blog, you will have a solid understanding of the different cutting methods, safety considerations, and tips for achieving optimal results when working with stainless steel.
Overall, mastering the art of cutting stainless steel opens up a world of possibilities for manufacturers, engineers, and DIY enthusiasts. With the right knowledge and techniques, stainless steel suppliers and fabricators can confidently create products that meet the highest standards of quality, durability, and aesthetics. So, let’s explore the realm of stainless steel cutting and unlock its full potential together.
II. Understanding Stainless Steel
- Stainless steel is a remarkable alloy composed primarily of iron, chromium, and varying amounts of other elements such as nickel, molybdenum, and manganese.
It possesses unique properties that make it highly desirable for a wide range of applications. Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, which is achieved through the formation of a passive chromium oxide layer on its surface.
This layer acts as a protective barrier against rust, making stainless steel ideal for applications in harsh environments. - Stainless steel also exhibits excellent strength, durability, and heat resistance. It can withstand high temperatures without losing its structural integrity, making it suitable for applications involving heat and pressure.
Additionally, stainless steel offers hygienic properties, making it a preferred choice for industries such as food processing and medical equipment manufacturing. - There are numerous types and grades of stainless steel, each designed to meet specific requirements. The most common types include austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, and duplex stainless steels.
Austenitic stainless steel, such as the popular grade 304, is non-magnetic and offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it widely used in various industries. - Ferritic stainless steel, like grade 430, is magnetic and has lower corrosion resistance but exhibits good formability and high-temperature strength. Martensitic stainless steel, such as grade 410, is known for its high strength and hardness.
Duplex stainless steel combines the qualities of both austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, providing enhanced strength and corrosion resistance.
- Choosing the right stainless steel for cutting is crucial to achieve desired results. Factors such as the intended application, environmental conditions, and desired mechanical properties must be considered. Different grades of stainless steel have varying machinability, hardness, and resistance to cutting forces.
Stainless steel suppliers play a critical role in guiding fabricators and manufacturers in selecting the appropriate stainless steel grade that suits their cutting requirements. By understanding the properties and characteristics of stainless steel, suppliers can ensure that their customers have access to the most suitable material for their cutting needs. - Furthermore, selecting the correct stainless steel grade contributes to the overall success of the cutting process. It affects the choice of cutting tools, cutting techniques, and the ability to achieve precise cuts while minimizing tool wear and distortion.
Stainless steel suppliers who provide expertise in material selection empower fabricators to make informed decisions and optimize their cutting operations. - In summary, comprehending the properties and different grades of stainless steel is vital for stainless steel suppliers and fabricators alike. It enables them to identify the most appropriate stainless steel for cutting applications, ensuring optimal results in terms of durability, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
By working together, suppliers and fabricators can create efficient and effective cutting processes that maximize the potential of stainless steel.
III. Tools and Equipment for Stainless Steel Cutting
A. Overview of common cutting tools for stainless steel
Cutting stainless steel requires the use of specific tools designed to handle its hardness and strength. Stainless steel suppliers offer a range of cutting tools suitable for various cutting techniques. Some common tools include:
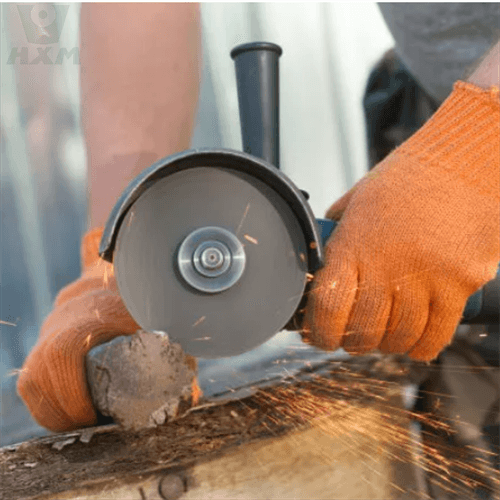
- Abrasive cut-off wheels:
These wheels consist of abrasive particles bonded together and are used with angle grinders or chop saws. They are effective for straight cuts and are available in different sizes and thicknesses. - Bandsaws:
Bandsaws equipped with high-speed steel or carbide-tipped blades are commonly used for cutting stainless steel. They offer precision and versatility, allowing for curved cuts and intricate shapes. - Plasma cutters:
Plasma cutting is a popular method for cutting stainless steel, especially for thicker materials. Plasma cutters use an electrically conductive gas to create a high-temperature plasma arc, melting and cutting through the stainless steel.
B. Discussion of their features, advantages, and limitations
Each cutting tool has its own features, advantages, and limitations when it comes to cutting stainless steel.
- Abrasive cut-off wheels:
These wheels are cost-effective and readily available. They provide fast cutting speeds and can handle thin sheets of stainless steel.
However, they may generate a significant amount of heat and create burrs or rough edges. - Bandsaws:
Bandsaws offer excellent precision and the ability to make intricate cuts.
They produce clean edges and can handle various thicknesses of stainless steel.
However, they may require more setup time and maintenance compared to other tools. - Plasma cutters:
Plasma cutters excel at cutting thick stainless steel quickly and precisely.
They provide smooth edges and do not create excessive heat-affected zones. |
However, they may be more expensive to purchase and operate, and the initial setup requires specialized equipment.
C. Safety precautions when using cutting tools
When using cutting tools for stainless steel, safety should always be a top priority. Stainless steel suppliers emphasize the following safety precautions:
- Personal protective equipment (PPE):
Wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing, to protect against sparks, debris, and potential injuries. - Secure workpiece:
Ensure the stainless steel workpiece is securely clamped or held in place to prevent movement during the cutting process. - Ventilation:
Work in a well-ventilated area or use local exhaust ventilation to minimize exposure to fumes and dust generated during cutting. - Tool maintenance:
Regularly inspect and maintain cutting tools to ensure their proper functioning and prevent accidents caused by worn-out or damaged equipment. - Training and knowledge:
Ensure operators are trained in the correct use of cutting tools and techniques, including understanding the limitations and potential risks associated with cutting stainless steel.
By following these safety precautions and using the appropriate cutting tools, stainless steel suppliers and fabricators can significantly reduce the risk of accidents, ensure a safer working environment, and achieve high-quality cuts in stainless steel.
In conclusion, stainless steel cutting requires specific tools and equipment designed to handle its unique properties. Stainless steel suppliers offer a variety of cutting tools, each with its own features, advantages, and limitations. However, it is crucial to prioritize safety by following recommended precautions and providing proper training to individuals handling these tools. By employing the right tools and adhering to safety guidelines, stainless steel suppliers and fabricators can effectively cut stainless steel and meet the demands of various industries.
IV. Techniques for Cutting Stainless Steel
A. Overview of various cutting techniques
When it comes to cutting stainless steel, several techniques are commonly employed:
- Shearing:
Shearing involves using a sharp-edged blade to make straight cuts through stainless steel sheets or plates.
This technique is ideal for high-volume cutting and is relatively fast and cost-effective. - Sawing:
Sawing utilizes specialized saw blades to cut through stainless steel. Band saws and circular saws equipped with the appropriate blades are commonly used.
Sawing provides precise cuts and is suitable for various thicknesses and shapes. - Plasma cutting:
Plasma cutting involves the use of a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to melt and cut through stainless steel.
It is effective for cutting thick stainless steel and offers high cutting speeds and accuracy. - Laser cutting:
Laser cutting utilizes a focused laser beam to melt and vaporize the stainless steel, creating precise cuts.
Laser cutting is highly accurate, suitable for intricate shapes, and provides a clean edge finish. - Waterjet cutting:
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water mixed with an abrasive substance to cut through stainless steel.
This technique is versatile, allowing for the cutting of various thicknesses and materials, and does not generate heat-affected zones.
B. Detailed explanation of each technique, including process, benefits, and applications
- Shearing:
Shearing involves placing the stainless steel between two sharp blades and applying force to create a clean, straight cut. It is commonly used in manufacturing processes, such as fabrication and sheet metal cutting.
Shearing offers high productivity and cost-efficiency, especially for large-scale production. - Sawing:
Sawing stainless steel with band saws or circular saws equipped with the appropriate blades allows for precise and controlled cuts.It is suitable for cutting stainless steel tubes, profiles, and sheets.
Sawing offers flexibility in terms of cutting angles and is commonly used in metalworking, construction, and fabrication industries. - Plasma cutting:
Plasma cutting utilizes a plasma arc to melt and cut through stainless steel. It is particularly effective for cutting thick stainless steel plates and structural components.
Plasma cutting provides high cutting speeds, versatility in terms of shapes and sizes, and minimal heat distortion. It finds applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and shipbuilding. - Laser cutting: Laser cutting utilizes a focused laser beam to melt and vaporize the stainless steel, resulting in precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones. It is ideal for complex shapes, intricate designs, and thin stainless steel sheets.
Laser cutting offers high accuracy, clean edges, and is widely used in industries like electronics, signage, and jewelry manufacturing. - Waterjet cutting:
Waterjet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water mixed with an abrasive substance to cut through stainless steel. It is suitable for various materials, including thick stainless steel, and offers the ability to cut intricate shapes with high precision.
Waterjet cutting does not generate heat and is commonly used in industries such as architecture, art, and manufacturing.
C. Comparison of the different techniques based on precision, speed, and cost
The choice of cutting technique depends on factors such as the desired precision, cutting speed, and budget.
Shearing and sawing techniques provide fast and cost-effective solutions for straight cuts.
Plasma cutting offers high cutting speeds for thicker materials, while laser cutting provides exceptional precision for intricate designs.
Waterjet cutting excels in versatility and precision, without generating heat.
Each technique has its own advantages and limitations, and stainless steel suppliers can provide guidance on selecting the most suitable technique based on specific cutting requirements.
By following these tips and best practices, stainless steel cutting can be performed effectively and with better results. Stainless steel suppliers can provide further guidance and recommendations based on specific cutting requirements, ensuring successful outcomes.
Remember, understanding how to cut stainless steel properly is crucial to achieving accurate and high-quality results while ensuring the safety of operators and maintaining the integrity of the material.
V. Tips and Best Practices for Effective Stainless Steel Cutting
A. Preparing the workpiece
for cutting
- Clean the surface:
Before cutting stainless steel, ensure that the workpiece is free from contaminants such as dirt, oil, or rust.
Use a stainless steel cleaner or solvent to clean the surface thoroughly. - Marking and measuring:
Accurate marking and measuring are essential for precise cuts.
Use a scribe or a permanent marker to mark the cutting lines on the stainless steel, taking into consideration the desired dimensions and shape of the final piece.
B. Choosing the appropriate cutting method based on the desired outcome
- Consider the material thickness:
Different cutting techniques are suitable for various thicknesses of stainless steel.
For thinner sheets, shearing, sawing, or laser cutting may be more appropriate, while plasma cutting or waterjet cutting can handle thicker materials. - Evaluate complexity and precision:
If you require intricate designs or complex shapes, laser cutting or waterjet cutting is recommended due to their high precision capabilities. For simpler shapes, shearing or sawing may suffice.
C. Maintaining tool sharpness and proper lubrication
- Sharpening cutting tools:
Regularly check and sharpen the cutting tools to ensure clean and efficient cuts. Dull blades can result in rough edges and increased cutting forces. - Lubrication and cooling:
Using appropriate lubricants or coolants during the cutting process helps reduce friction, heat, and tool wear.
Consult with stainless steel suppliers or tool manufacturers to determine the best lubrication method for the specific cutting technique and material being used.
D. Minimizing heat and preventing distortion during the cutting process
- Optimize cutting parameters:
Adjust cutting speed, feed rate, and power settings based on the type and thickness of the stainless steel.
This helps minimize heat buildup and potential distortion. - Use proper clamping and fixturing:
Securely clamp the workpiece to prevent movement during cutting, which can cause inaccuracies and distortion.
Use suitable fixtures to support the material and distribute cutting forces evenly.
By following these tips and best practices, stainless steel cutting can be performed effectively and with better results. Stainless steel suppliers can provide further guidance and recommendations based on specific cutting requirements, ensuring successful outcomes.
Remember, understanding how to cut stainless steel properly is crucial to achieving accurate and high-quality results while ensuring the safety of operators and maintaining the integrity of the material.
VI. Safety Considerations
A. Importance of personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Eye protection:
Wear safety goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes from flying debris and sparks generated during the cutting process. - Hand protection:
Use cut-resistant gloves to safeguard your hands from sharp edges and potential injuries. - Respiratory protection:
When cutting stainless steel, especially with processes like plasma cutting or laser cutting, there may be fumes, gases, or fine dust particles released.
Wear a respirator or mask approved for metal fumes to prevent inhalation of hazardous substances.
B. Handling and disposal of stainless steel scraps
- Sharp edges:
Be cautious when handling stainless steel scraps, as they can have sharp edges that may cause cuts or punctures. Wear gloves and use appropriate lifting techniques to avoid injuries. - Scrap disposal:
Dispose of stainless steel scraps responsibly. Consult local regulations and recycling guidelines to ensure proper disposal methods. Stainless steel suppliers can provide guidance on recycling options and waste management practices.
C. Proper ventilation and control measures for fumes and dust
- Adequate ventilation:
Ensure the cutting area is well-ventilated to minimize the accumulation of fumes and dust. Use exhaust systems or fans to improve air circulation and remove airborne contaminants. - Dust collection systems:
For processes that generate significant amounts of dust, such as sawing or grinding, employ dust collection systems or vacuum systems to capture and contain the particles, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and maintaining a clean work environment. - Control measures:
Implement control measures to reduce exposure to fumes and dust, such as enclosing the cutting area or using local exhaust hoods. Regularly inspect and maintain ventilation systems to ensure their effectiveness.
It is essential to prioritize safety when cutting stainless steel. By following these safety considerations, you can protect yourself, prevent accidents, and maintain a healthy working environment. Consult with stainless steel suppliers or safety professionals for specific recommendations based on your cutting processes and equipment.
Remember, knowing how to cut stainless steel is not only about achieving precise results but also about safeguarding your well-being throughout the cutting operation.
VII. Conclusion
A. Summary of key points discussed in the blog:
- Stainless steel cutting plays a vital role in various industries due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
- Cutting stainless steel poses challenges such as its high strength, hardness, and tendency to work-harden, requiring careful consideration of techniques and tools.
- Understanding stainless steel properties, including its composition and grades, is crucial for selecting the appropriate material for cutting applications.
- A wide range of cutting tools and equipment is available for stainless steel cutting, each with its features, advantages, and limitations. It is important to choose the right tool for the specific task.
- Safety precautions, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), proper handling and disposal of stainless steel scraps, and adequate ventilation, are essential to ensure a safe working environment.
- Various cutting techniques, such as shearing, sawing, plasma cutting, laser cutting, and waterjet cutting, offer different benefits in terms of precision, speed, and cost. The choice of technique depends on the specific requirements of the project.
- Tips and best practices, such as preparing the workpiece, selecting the appropriate cutting method, maintaining tool sharpness and lubrication, and minimizing heat and distortion, contribute to effective stainless steel cutting.
Proper techniques and safety measures are paramount in achieving successful and efficient stainless steel cutting. Following best practices not only ensures quality results but also minimizes the risk of accidents, injuries, and damage to equipment. By prioritizing safety and employing the appropriate cutting techniques, stainless steel cutting operations can be performed effectively and with confidence.
In conclusion, stainless steel cutting is a valuable skill that opens up opportunities in various industries. By understanding the properties of stainless steel, selecting the right tools and techniques, and prioritizing safety, you can overcome the challenges associated with cutting this versatile material. Don’t hesitate to reach out to stainless steel suppliers for guidance on material selection and other technical aspects. With knowledge, practice, and attention to safety, you can confidently embark on stainless steel cutting projects and unlock the full potential of this remarkable material.
Get A Free Quote
Trust us to be your excellent stainless steel suppliers, we will answer in 12 hours. Or you can send an emali to us directly. (export81@huaxia-intl.com)
Related Posts
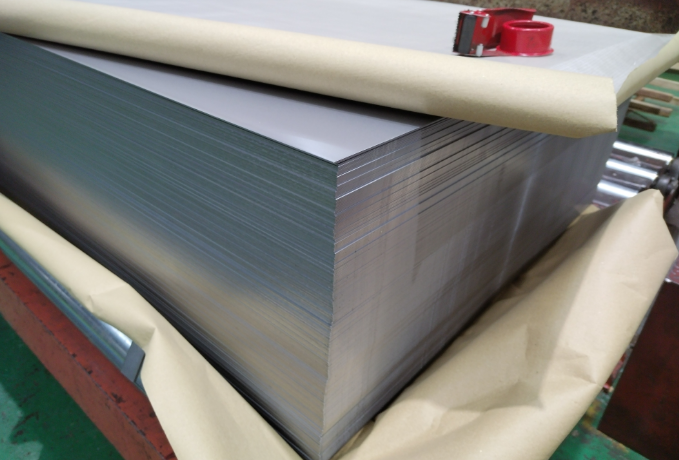

Protective Measures for Stainless Steel in Water Environments
Stainless steel, as an extensively utilized alloy material, finds applications across numerous working scenarios. However, it is crucial to emphasize that when stainless steel is

Performance Characteristics and Applications of 303 Stainless Steel
303 stainless steel, as a type of stainless steel containing sulfur and selenium, not only exhibits high machinability and resistance to high-temperature sticking but also
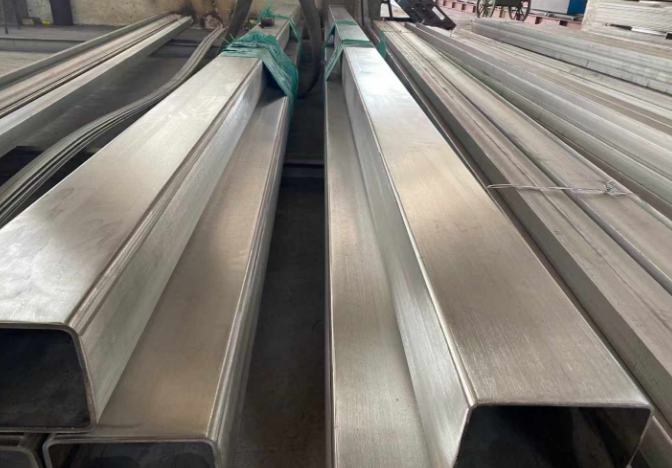

Properties, Characteristics and Applications of 416 Stainless Steel
As an outstanding martensitic stainless steel, 416 stainless steel boasts a unique chemical composition that endows it with superior magnetic properties, good corrosion resistance, ease
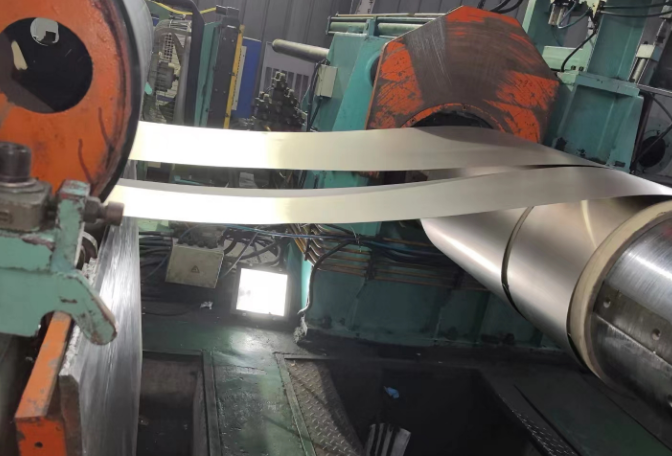

Advantages of Hot Rolling Process in Stainless Steel Manufacturing
Stainless steel, a ubiquitous metallic material, finds extensive applications across various sectors such as construction, food processing, and healthcare. Enhancing the reliability and durability of

5 Methods to Enhance the Strength of Austenitic Stainless Steel
Stainless steel, as a crucial and widely utilized steel type, enjoys extensive applications in civil and industrial sectors due to its high corrosion resistance, excellent
 :+86-13012867759
:+86-13012867759  :export86@sino-stainless-steel.com
:export86@sino-stainless-steel.com








The Secret to Eliminating a Double Chin
Chin Filler: The New Way To Get Rid Of A Double Chin
Can Chin Filler Reduce Double Chin?
Yes, chin filler is increasingly being used to reduce the appearance of a double chin. By adding volume
and contour to the lower face, it can help create a more defined and youthful jawline.
Chin Fillers: A Safe And Reliable Way To Improve Your Double Chin
Chin fillers are considered safe and reliable for improving the double chin. They are
non-surgical, require minimal downtime, and often come
in the form of injectable treatments using natural materials like hyaluronic
acid.
Can Dermal Fillers Remove Double Chin?
Dermal fillers can help address a double chin by augmenting volume in the lower face.
However, the effectiveness may vary depending on the individual’s facial
structure and the severity of the double chin.
Looking For A More Natural Look? Try A Combination Of Fat Dissolving Injections
And Dermal Fillers
For those seeking a more natural result, combining fat-dissolving injections with dermal fillers can provide a balanced approach.
This method targets both volume loss and sagging skin, creating
a smoother and more youthful appearance.
About Author
Written by Author Name, a professional in the field of cosmetic treatments and aesthetics.
Pages
Explore more articles on our Pages section.
Categories
This article belongs to the Categories section.
Legal Steroids: What Works, What Doesn’t, Precautions, Alternatives
What Do Legal Steroids Work For?
Legal steroids are designed to aid muscle growth,
fat loss, and performance enhancement. They
work by mimicking the effects of anabolic steroids without the latter’s illegal status.
Potential Benefits
Muscle gain
Fat loss
Increased strength
Enhanced recovery
What Don’t Legal Steroids Work For?
While legal steroids can be effective, they don’t work for
everyone. Factors like genetics, diet, and exercise play significant roles in their
effectiveness.
Limitations
Results may vary
Cannot exceed natural limits
Require a supportive lifestyle
Precautions to Consider
Before using legal steroids, consider these precautions:
Health Risks
Hormonal imbalances
Acne and hair loss
Dermatological issues
Legal and Ethical Use
Ensure compliance with local laws and ethical usage guidelines to avoid legal trouble.
Alternatives to Legal Steroids
If legal steroids aren’t suitable for you, consider these alternatives:
Natural Supplements
Protein supplements
Balanced diets
Exercise programs
Consult Professionals
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new regimen.
Conclusion
Legal steroids can be beneficial but come with considerations.
Always prioritize health, safety, and ethical practices when deciding to use them.
Legal Steroids: Do They Work and Are They Safe?
Are you considering using legal steroids to enhance your fitness goals?
While they can offer benefits, it’s crucial to understand how they
work, their limitations, and the precautions necessary.
### Health Conditions
Legal steroids are often used by individuals looking to build muscle mass or improve physical performance.
These conditions include:
– Muscle wasting due to disease or aging.
– Reduced strength in older adults.
– Recovery after surgery or injury.
### Condition Spotlight
– **Muscular Dystrophy**: Legal steroids can help maintain muscle mass
in patients with this condition.
– **Healthy Aging**: They may aid in maintaining muscle function and preventing age-related decline.
### Why You Shouldn’t Use Anabolic Steroids
While legal alternatives exist, anabolic steroids are risky.
They can lead to severe health issues like liver damage, cardiovascular problems, and psychological
effects like paranoia or aggression.
### The Takeaway
Legal steroids can be safe when used responsibly,
but they’re not for everyone. consult with a healthcare professional before deciding.
### Alternative Ways to Build Muscle Mass and Strength
If you’re cautious about legal steroids, consider these alternatives:
#### Creatine
A proven supplement that boosts strength and endurance.
#### Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP) Inhibitors
These can help maintain muscle mass during use.
#### Dimethylamylamine (DMAA)
Known for its ability to enhance energy and focus during workouts.
### Create a Good Weight-Training Routine
Start with compound movements like squats and deadlifts, incorporating splits or circuits into your routine.
### Follow a Healthy, Muscle-Friendly Diet
Focus on protein-rich foods, sufficient calorie intake, and stay hydrated.
Consider consulting a nutritionist for a personalized plan.
### Work with a Personal Trainer
Professional guidance can help you stay motivated and ensure proper form.
### Use a Fitness App
Track your progress and create routines with apps like MyFitnessPal or Freeletics.
### Lessons from Experts
Experts advise that while legal steroids may work, natural methods are safer and more
sustainable in the long term.
### This Just In
Recent studies highlight the potential benefits of legal steroids
but also emphasize the need for caution and professional oversight.
### Top Reads
Explore articles like “The Best Protein Powders for Muscle Building” or
“How to Start a Weightlifting Routine.”
### Video Series
Watch guides on how to use legal steroids effectively, with tips on dosage and safety.
### Find Your Bezzy Community
Join forums or groups to connect with others who share your fitness goals.
### Follow Us on Social Media
Stay updated on the latest in fitness trends and reviews.
—
This article provides a comprehensive overview of legal steroids, their benefits,
risks, and alternatives. Always prioritize your health and consult with a healthcare professional before making
any decisions.
Battle ropes will enhance your work capability,
endurance, and pace, permitting you to perform higher in other areas of your health and in sports activities.
Battle ropes will make muscle imbalances and weak
muscular tissues obvious actually shortly. What’s even better is, they may improve them rapidly
too, and you don’t really need to think too much about it.
Simply go in regards to the exercise and your weaker facet
will catch up and those smaller, typically forgotten muscle tissue like your grip, forearms,
and hip flexors might be focused it does not matter what you do.
Of course, if you need to develop specific muscular tissues,
do what you should with dumbbells and the like, there’s nothing wrong with that.
Nonetheless, if you want a fast and effective workout, then battle ropes are top-of-the-line training instruments that exist
for that.
TRX Face Pulls primarily goal the rear deltoids, upper again, and rotator cuff
muscular tissues. This exercise aids in strengthening shoulder muscles whereas selling higher posture by engaging the muscles responsible for
retracting the shoulders. As A Result Of of the big selection of advantages, TRX face pulls complement resistance band shoulder workouts like pull-aparts.
Cut Up jumps require a good quantity of stability and core energy and will create explosive movements that build leg energy.
This depends on how a lot room you need to work with and your fitness objectives.
If you are going to be coaching in your yard, you want to be able to buy any dimension you’d like, so choose one that works
along with your health aim.
Make sure your shoulders do not slouch and spherical
forwards throughout this train. This train focuses on energy production somewhat than endurance.
Work exhausting for shorter bursts rather than making an attempt to preserve vitality.
All The Time make sure your physique stays in a straight line, don’t enable your
torso to lean forwards.
One of one of the best things about cable stations is the ability to regulate the machine load increments.
Every rep must be controlled, with a give consideration to intense muscle contraction. Focus on creating your own resistance with gentle weight before moving
as much as the heavier weight plates.
To help identify the supply of your ache and another
points, your doctor may ask for certain checks. Any harm to the bones that comprise your shoulder joint might be visible on an X-ray.
Possibly you overdid a task like painting, otherwise you damage it in a fall or other accident.
Pain that’s “referred” indicates that there’s an opportunity it comes
from issues in other parts of your body.
To improve shoulder vary of motion and adaptability, strive the towel shoulder
stretch. Train promotes blood circulate, flexibility, and power in the surrounding
muscular tissues of the joint, all of which help
the therapeutic course of. This exercise has to really feel prefer it goes into your higher again and behind your shoulder.
A cable shoulder Exercise is very really helpful for anyone interested in constructing a wider shoulder
and who needs to gain energy. Lastly, if you’re in search of one more effective shoulder exercise that you are capable of do with
a cable, try the straight arm lat pulldown. Half kneeling excessive cable row rope is an incredible exercise that
effectively works many muscle tissue, together with the shoulder, back, wing, and trapezius muscle tissue.
The cable shrug is a variation of the
shoulder shrug and top-of-the-line higher trap cable workout routines to construct
the upper back’s trapezius muscle. You can do that exercise using one arm at a time, allowing you to change the range
of motion by adjusting the start or end place. In Distinction To dumbbell raises the place
the resistance varies in the course of the lift, the cable pulley affords a
uniform resistance all through the motion.
Some discover it well-made and functional, while others report points like the hanger bending or the line coming off the pulley.
The hardware is praised, however some customers mention it is made with cheap materials
and will not final lengthy. If you’ve been following me on YouTube, I most likely don’t have to tell you when to carry out this train. If you’re going to do 12 reps of those, make sure it’s 12
units of 1. Travel is the monitor your hands and elbows take the rope or cable
as you pull. The square stance regulates the quantity of weight you need to use and makes it tough to overload it to the purpose the place it degrades
your type on that exercise. If you attempt to go
so heavy that you’re getting pulled forward, you know you’re going too heavy.
The different necessary factor to pay attention to is the position of your arms and elbows at the finish level of the
movement. Instead, seize it in an underhand grip along
with your thumbs backward. This provides you the exterior rotation of the shoulder with elevation which
is what we would like. You don’t want to be doing this, especially if you do your
face pulls as usually as I’m going to recommend you do! You’d be accumulating lots of
repetitions in an internally rotated shoulder position with elevation. One of the most common errors when performing the face
pull is the incorrect placement of the anchor level
of the band or the cable.
Any time you’re going overhead, you’re biasing the lengthy head of the triceps brachii.
This is a very comparable train to the 2nd on this list – it’s simply the single-arm model.
It’s a good suggestion to include each double-arm and single-arm variations.
This allows you to work in your side-to-side deficiencies and provides variety.
If you are doing a stand-alone battle rope workout, it can range, however usually not extra than 30
minutes is right. For a stand-alone exercise, you should rest about twice
as lengthy as your sets. As for heat ups, 5 minutes is plenty of time with battle
ropes to get the blood pumping. For this train, you’ll be creating
force that generates an arc-style wave down the rope towards the anchor point.
Trapeziuses are muscle tissue that begin at the base of the neck
and finish on the upper again. They also create a further stimulus for the shoulders,
though, and can allow you to to sculpt a extra well-rounded higher physique.
Begin by attaching the straight bar to the cable machine and adjusting the cable to its lowest level.
Subsequent, comply with the steps under to complete the cable
shoulder workout.
For more data relating to battle ropes check out extra articles at the Onnit Academy.
If you are a full newbie to battle ropes you’ll need to read through Corey Beasley’s article, Novices Information to Battle
Ropes. It is a really complete guide to battle ropes for newbies and superior athletes alike.
Begin in a half squat position, make positive you are to not far on the balls of your
ft, as this will lead to forward monitoring of
the knee over the toe.
This is an easier variation of the facility
slam and there shall be a larger emphasis on the higher body
while doing the double waves. In addition to utilizing battle ropes
for shoulder muscle development, there are different
shoulder protocols to enhance power and mobility.
These again muscle tissue are activated with the up-and-down motion of swinging the battle ropes.
Over time, you’ll see not simply energy but in addition definition in your shoulders that
makes all the trouble price it. Stick with these cable workout routines –
they’re a game-changer for anyone severe about their shoulder game.
For the Cable Y elevate, begin by standing in entrance of the cable machine.
The decrease traps are actually necessary for creating stability of the scapula
as we increase our arms up over our head. Performing
the face pull with this additional arm raise helps us give them
some a lot wanted consideration. So, if I had been to attempt to do full vary of movement where my arms are out in front of me getting some scapular protraction, after which I come back into the face pull, I hit
a wall. I don’t have the strength as a outcome of this
band obtained too hard too quickly. How will you implement these workout routines into your exercise routine?
Embrace the importance of this information as it can considerably influence your shoulder strength, stability, and total posture.
Executing this train with proper kind and control not
only minimizes the danger of damage but additionally maximizes its effectiveness,
selling optimum engagement of the muscle tissue.
Workout Routines of this sort are sometimes applied as a means of maintaining conditions similar to arthritis underneath control, and
as a part of rehabilitation after surgical procedure.
Whereas most range of movement workout routines could be
performed without supervision, some are supposed to be carried
out under the path of a helper or physical therapist.
Shoulder ache is common, however it might be prevented and treated.
Being unable to do daily duties could be severely
affected by shoulder ache. Even after you start
to really feel better, keeping up with the workouts and treatments will
help maintain the ache from returning. To relieve
ache and promote recovery, you would possibly attempt house treatments along
with shoulder workouts. Wall pushups concentrate on the muscular tissues of the upper body, including the arms, shoulders,
and chest.
The alternating waves with kneeling get-up is precisely because it sounds.
You might be performing kneeling get-ups as you do the alternating waves.
With that, working towards the tall-kneeling wave and half kneeling wave we showed you earlier earlier than attempting this
exercise, which combines all three variations, can be a smart transfer.
However, as all the time, it is essential to consult a licensed bodily therapist
for personalized guidance tailor-made to your particular needs.
This is as a result of cables provide fixed tension throughout the entire vary of motion, which helps enhance strength and sculpt your muscles from
head to toe. This exercise is similar to the medication ball slam as a outcome of it’s all about power.
Due to the battle rope power slam being an influence exercise, the sets shall be shorter as the major
target here is constructing explosive energy and never muscular endurance.
For a start, carry out 2 to three units of 10
to 12 repetitions to familiarize yourself with the motion.
The shoulder and scapular stabilization for the hand and arm that’s planted is firing way more through this dynamic movement than just a static maintain. The dynamic arm, shoulder, scapula,
chest, and shoulder can be tremendously extra engaged than just holding a static place.
This is a perfect approach to level-up your planks, or practice your
athletes which are looking for improvements in the stability and dynamic energy of their upper body.
Shoulder workouts are essential for constructing power, stability, and aesthetics.
Using a cable rope allows for controlled resistance,
making it a superb tool for focusing on the deltoids, trapezius, and rotator cuff muscular tissues.
He presently lives in Massachusetts and continues to
compete in powerlifting. The design of the cable machine means a extra
joint-friendly exercise expertise. They alleviate the burden placed on stabilizing muscle tissue and joints which are often careworn during compound barbell and dumbbell movements.
This makes them a greater choice for preserving your joints wholesome.
Doing rope crunches can make performing functional movements a lot easier
for the explanation that train reinforces the core muscles.
As A Outcome Of it’s performed leaning forward against an incline bench, this exercise positions the arms in such a means
that it minimizes the involvement of other muscle
groups.
With the Whip, you’ll essentially be creating horizontal waves.
Be sure switch the half kneeling place each set (so right leg in front
then left leg in front). Maintain these cues and suggestions in mind, as they apply
to a lot of the exercises to come.
Right Here, determine pro Nicole Wilkins demonstrates how to execute
this distinctive routine created by Gino Caccavale, New York
City–based coach and founder of Muscle in Motion. You’ll blast severe energy
and construct modern muscle—plus add serious fun to your weekly routine.
Kurtis Ackerman is a personal trainer residing in Southern California.
He competed in powerlifting and Strongman in his youthful years.
Now he trains all kinds of clientele however makes a speciality of working
round accidents.
It promotes strengthening of your postural muscles, serving
to to combat society’s ever present tech neck
and rounded shoulder concern. As you will see with the workout routines on this article, there are such a lot of different battle rope workout routines and ways to make use
of them to target or emphasize specific muscular tissues.
So this was all about tips on how to use a cable machine to train the entire part of
your shoulders.
Moreover, it’s possible to incorporate aspect, front,
and again lunges whereas utilizing the battle ropes to further
work out the legs. Making certain your shoulders are warmed up means much less risk of harm and a greater chance to build power effectively.
Carry the handle to shoulder top, then slowly lower it again down. This exercise retains pressure in your shoulders,
making them work exhausting. Doing this train keeps pressure in your
shoulder muscular tissues all via the move.
As for fitness objectives and health ranges, the longer the rope,
the higher no matter what your objective is.
The thickness of the rope should be more of a concern when shopping for (in terms of difficulty),
as you can purchase the longest battle rope attainable for your space.
Though battle ropes present lots of benefits, there are some
disadvantages that ought to be addressed as properly.
Let’s rapidly go over the pros and cons of battle ropes that will assist you resolve if its a purchase
that is right for you particularly. Battle ropes, that are also called battling ropes or heavy
ropes, are a health coaching implement used to enhance strength and conditioning.
As the name suggests, it is a rope, however it is not simply any rope.
The rope is thick, heavy, and lengthy, giving it significant resistance and movability.
Nutrafirst BCAA Powder complement is a potential product for gym-goers to sail via their vigorous
training regimes easily. The meticulous efforts by team Nutrafirst have given your
health objectives a actuality with BCAA Powder. Nutrafirst BCAA price is pocket-friendly and could be availed by every health aspirant.
The willingness to remain active won’t are available
the greatest way of your dreams when one of the best Nutrafirst BCAA Powder
supplement in India gets included into your routine.
They’re a very pure and concentrated method to ship
vitamins to your muscle tissue, and infrequently work at the
facet of other elements in a pre-workout, intra-workout, or post-workout supplement.
If plain BCAA powder isn’t your factor, an various choice is
to take a capsule. We specifically looked for supplements that made it easy to take a dose of three to six grams, two to
three times per day.
Nutrafirst.in is a community of high quality nutritional supplement On-line buying.
We aim to provide protected and effective weight administration, sports activities nutrition, health and general health applications to assist clients look higher, feel higher and
perform higher. For many individuals following the popular ketogenic diet, it
could be complicated to know which dietary supplements can be
used to reinforce their fitness goals without breaking ketosis.
BCAA has only a few energy and can be utilized safely in weight loss diets corresponding to a keto food regimen or throughout
intermittent fasting. BCAA is ideal as a workout complement for coaching in a
fasted state (81). For a maximum efficiency increase, you’ll
have the ability to think about taking each BCAA and pre-workout dietary supplements.
Although they’ve some widespread properties, they work in several methods to
boost your exercise.
With anything that tastes nasty, it is at all times easier to drink it chilly.
She was utilizing the BCAA powder to prevent muscle loss
while dieting, so popsicles worked nice. Now we all know that we want each BCAAs and
EAAs to support our muscle tissue with protein synthesis.
For occasion, when you primarily interact in high-intensity workouts, you might want to consider a
method that emphasizes energy-boosting elements alongside BCAAs.
Many products also characteristic other performance-boosting compounds,
similar to caffeine, citrulline, or beta-alanine, which can synergistically work with BCAAs
to improve general workout efficacy. Due To This Fact, a well-rounded formulation can further enhance
both muscle efficiency and endurance throughout high-energy
activities. Branched-Chain amino acids consisting
of valine, leucine, and isoleucine. These are all essential amino acids that the physique wants to stay wholesome.
They play an important function in providing the muscle tissue with
the protein it must grow strong. Whereas regular
amino acids are essential, they aren’t quite as helpful for strengthening muscles and
promoting recovery as BCAAs.
You can take BCAA dietary supplements in the form of capsules or combine the powder supplement into your workout
milkshakes. These are handy to carry round, straightforward to take any time, and anyplace as properly.
On the other hand, train additionally makes us really feel
good as a result of pleased hormone ‘serotonin’ getting launched during the exercise.
As our muscles use up BCAAs, this triggers the conversion of the amino acid tryptophan to serotonin in our brains (19).
These body aches, that are likely to develop 12 to 24 hours after your workout, are called delayed onset muscle soreness
(DOMS) (14). Tiny tears within the muscle tissue in the course of
the train are believed to trigger DOMS, although the exact cause is but to
be identified by researchers (15). To help right for this,
I seemed on the quantity of every important amino acid
in six different EAA dietary supplements and averaged them out to get an idea
of what a “typical” profile looks like.
Add one scoop to ounces of any beverage of your alternative and give
your body the help to perform better. It could be taken as
a pre-workout for vitality or post-workout for restoration. On non-training days, CoreSeries
BCAA Glutamine could be taken within the morning, for improved recovery.
Each of the BCAA supplements on our listing is great in its own way, and the way well they work for you is decided by your training and life-style choices.
So when you have been questioning whether or not you want to add a BCAA complement to
aid in your health journey, then contemplate one of many options listed above.
The Xtend Sport BCAA Powder helps hold the body flooded and
fueled with electrolytes. This allows you to maintain your performance as
tight as possible, with subsequent to no dips in efficiency high quality.
Blackwolf is an all-natural powder drink pre-workout complement which
might enhance your workout. Whether Or Not you’re a seasoned athlete or
new to fitness, understanding the function and benefits of BCAAs can significantly impression your nutritional technique
and overall wellness journey. One Other cool thing about BCAAs is how they
help with weight management.
Several studies have confirmed that creatine increases train performance,
muscle mass, and power (50, 51). Creatine supplements boost energy and reduce
muscle breakdown in addition to the danger of damage during
exercises (52, 53). Thus, through the use of BCAA supplements,
one is prone to have improved power, endurance,
muscle mass, and exercise restoration. It promotes the
formation of latest muscle proteins, maintains muscle tissue and reduces exercise
exhaustion. Some of the most important brands with BCAA powders and capsules out
there in India are Optimum Diet, MuscleBlaze, Bigmuscles Vitamin and so on.
During exercises, essential amino acids assist our bodies construct muscles by aiding in protein synthesis.
BCAA powders are usually suitable for most individuals, particularly these involved in regular physical activity, similar to athletes, bodybuilders,
and health enthusiasts. They can assist both performance and restoration, making them a valuable addition to many training regimens.
BCAA when taken as a pre-workout supplement boosts your stamina, reduces muscle harm,
and exercise-induced fatigue, thus enhancing your exercise performance.
If you may be wondering which one is the winner, the reply once more is determined
by your health targets. If your focus is on muscle constructing,
then go for the BCAAs as higher doses of BCAAs will do you extra good than a general
pre-workout complement. While some pre-workout dietary supplements comprise stimulants corresponding to caffeine (72).
Pre-workout supplements are meant to enhance your power levels,
focus, and ultimately your exercise performance.
The best time to take BCAA supplements is post-workout as they promote muscle synthesis (44).
Individuals with this type of deficiency additionally
typically expertise problems with sustaining a wholesome weight.
It is essential to take a look at the essential list of options for every amino acid supplement.
This includes the specifics of the formulation so you realize precisely what’s in it.
Producers generally tend to change their formulas, so you should get this data.
Xtend incorporates 7 grams of BCAAs per serving,
including 3.5g of leucine and 1.75g of isoleucine and valine.
The main good factor about utilizing Xtend BCAAs
is they are the quickest absorbing type of proteins for improving muscle recovery and muscle growth.
I share my health coaching expertise in addition to the sports science analysis I’ve
done on the many advantages strength constructing, train, & good consuming habits offer us.
While it might be tempting to go for probably the most reasonably priced
option, it’s important to assess the general worth you’re getting for your cash.
Cheaper powders might comprise low-quality elements or decrease doses of BCAAs, in the end diminishing their effectiveness.
It’s important to think about serving measurement, the number of servings per
container, and the overall formulation when contemplating the
worth. In addition to assessing the source of
BCAAs, it’s essential to check for added elements that complement the primary formulation. Many
top products will embrace electrolytes, vitamins, or even performance-enhancing compounds
like beta-alanine and citrulline. These supplementary ingredients
can improve hydration, vitality levels, and overall exercise efficiency,
making the product extra beneficial than BCAAs alone.
Additionally, BCAA pre-workout powders are known for reducing muscle soreness and damage, which may considerably impression restoration times.
PVL Gold Series EAA + BCAA Full may help you
remodel your exercises and exceed your health goals. Not only does it have an excellent ratio of BCAAs, it
additionally incorporates different amino acids. This makes it great for individuals who do marathon exercises, or who need a slower-acting source of gasoline
for his or her muscular tissues. For a very lengthy time, BCAAs (branched-chain amino
acids) have been the only amino acids that science believed necessary for active restoration post-workout.
Important amino acids aid within the building of protein in your body, generally recognized as protein synthesis.
Pure important amino acids and no sketchy components, VitaMonk is at the prime of its recreation with this EAA complement.
Designed for athletes on the hunt for high EAA dietary supplements
that can promote wholesome muscle growth and help
protein synthesis.
Luckily, you can’t overdose on these amino acids,
as your physique gets rid of any extra. However, some potential
BCAA unwanted effects might occur when you soak up an excessive amount of, including
nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, bloating, poor sleep, or a lower
in blood pressure. You can take BCAA supplements in the type of capsules or
powder as much as 3 occasions daily, however
the perfect dosage varies relying on the product concentration and
your weight.
Its blend of 13 amino acids ensures your body has the important building blocks for efficiency and restore.
NSF certification adds belief, making it a dependable alternative for athletes and fitness fanatics alike.
One of the first causes folks opt for BCAA pre-workout
powders is their ability to boost vitality ranges. Throughout intense exercises, the body
can deplete its shops of amino acids, leading to fatigue and diminished efficiency.
Anvarol has been chosen for its strategic formulation that promotes phosphocreatine synthesis, key for sustaining energy throughout intense exercises.
It stands as a authorized and safe option for those aiming to retain lean muscle during
slicing cycles whereas shedding fat effectively. Customer testimonials
constantly reward D-Bal MAX for its effectiveness, marking it as a top-tier choice for serious athletes and health lovers.
Excessive consumption of BCAA dietary supplements might have unfavorable effects on temper and could probably enhance the
risk of cardiovascular disease. Analysis suggests that the metabolism of amino acids,
like BCAAs, may be concerned within the development of coronary heart illness.
The powder form BCAA dietary supplements usually are available in a flavoured combination that’s designed to be combined with water,
though some non-flavoured powders are additionally obtainable.
That being mentioned, many corporations also produce unflavoured powders
(like our top choice on this guide) which don’t comprise any unnecessary additions.
That all being stated, many bodybuilders and gym-goers select to consume a BCAA supplement to up their consumption of these three essential amino acids.
Clear Labs CoreSeries BCAA Glutamine presents all the benefits of a BCAA complement with
the further advantage of L-glutamine for optimum intestine health in the method.
Designed for one of the best BCAA for restore and recovery, Transparent
Labs has crafted a 100 percent clean formula with a transparent
label so you know precisely what you are getting. For
other functions, you possibly can follow the dosage advice in your supplement’s packaging.
If you purpose to spice up your muscle progress by taking a BCAA
supplement, guarantee you’re looking after your protein consumption and getting sufficient BCAAs.
Each serving of HydroBCAA has 7g BCAA + 3g EAA with zero sugar, zero carbs, no synthetic colors or flavors.
You’ll additionally get electrolytes and Sustamine for sufficient
hydration so you presumably can keep on performing.
BCAAs help in muscle maintenance, preservation, and restoration but do not immediately contribute
to muscle hypertrophy like creatine does. As mentioned
above, your choice between BCAAs and creatine is determined by your
objectives. BCAAs and creatine could be stacked for one of the best results inside recommended dosages.
While the common advantages are well-known, for these new to their fitness journey, they work
differently and serve distinct purposes.
There’s an increased level of alertness and focus but it’s not
overpowering. Except you completely can’t stand the watermelon taste, there is not any reason to not buy your
Amino Vitality + Electrolytes from Costco. These statements haven’t been evaluated by the FSSAI or
any governing authority. This product is not supposed to diagnose, deal with, cure
or forestall any illness. Clients dislike the chalky texture of the dietary supplement.
They point out it has a white and chalky consistency, and
does not scent or taste pretty much as good.
They say it works properly as a pre-workout drink and helps them stay hydrated.
Nonetheless, some clients have reported stomach issues like cramps
and diarrhea. There are combined opinions on the taste and worth for money.
Optimum Nutrition Amino Vitality stands out as a flexible pre-workout alternative with its
unique mixture of amino acids, caffeine, and flavor choices.
Nevertheless, it is important to contemplate its proprietary blend and synthetic parts.
CLA works to minimize back body fats by stopping fats accumulation in fat cells.
Fats usually enters the fats cell through a door that’s
managed by an enzyme that acts as the vital thing. When the door is locked, fats cannot enter the cells and they are prevented from growing in measurement.
The much less fat present in the cells, the
smaller and fewer mature they turn out to be. The elevated breakdown of fat helps
to fuel and protect muscle mass, which in flip will increase lean muscle mass.
ENERGY you may get the power + focus to realize your goals and
take on whatever life throws at you. ESSENTIAL
AMINO ENERGY is scientifically designed to assist your vitality
needs and your long-term training. Prospects discover the pre-workout drink helpful for his or her workouts.
Our database accommodates an in depth assortment of
over four,000 Costco consumables including meals, drinks, alcohol, vitamins, and dietary supplements.
The energy mix is effective and the electrolytes and BCAAs/amino acids are a
very nice bonus. For anytime energy assist or for post
workout amino support, the really helpful scoops are going to be 2-4.
It can be used anytime that an vitality enhance is needed;
pre-workout for vitality & hydration, or as a sports drink substitute for post-workout recovery
and rehydration. Customers discover the drink has an excellent
taste, much like grape soda.
It supplies them with the energy they want and helps them stay hydrated.
They appreciate the quality of the product and the right amount of caffeine.
The drink accommodates zero sugar, helping them
kick their sugar habit.
Clients have different views on the style of the nutritional supplement.
Some discover it pleasant and energized without the caffeine crash.
The synthetic sweetener sucralose has negative unwanted facet effects.
It helps motivate them to exercise and makes their workouts easy.
Optimum Diet Essential Amino Energy drink has a mix of ingredients and has an appealing taste with a modest
amount of caffeine. Subsequently, consuming Amino Power drinks every
day isn’t really a good idea. Drink it when you want a
strong boost but by no means depend on them for general energy.
This supplement powder is completely different from the ever in style Amino Vitality as this complement contains added electrolytes.
Prospects recognize the energizing impact of this dietary complement.
They discover it helps them get via their exercises,
has a pleasant taste and no smell. I usually wake
up round 7, have this drink by 8 and break my fast round 4
for reference. I Am Going To begin off by saying I do not work for any firm affiliated with this product however holy moly is these
items nice.
The amino acids may cause tingling in the palms and itching.
They discover it helps them keep targeted and energized without jitters.
The added caffeine and electrolytes hold them hydrated
all through the day, helping them feel awake and well-rested.
Its well-balanced formula supports muscle restoration, enhances exercise performance, and supplies
clean, sustained power with out extreme stimulants.
I haven’t but taken a 6 scoop serving as a pre-workout, but I do start to
really feel the vitality ramp up after 2-3 scoops.
I doubt this is able to be equivalent to an precise pre-workout complement, however I even have no
doubts this will enhance your energy degree within the
gym. CLA is a remarkable dietary complement derived from sources like
safflower and sunflower oil, and found naturally in grass
fed meats and dairy in addition to the yolk of an egg.
Therefore, Amino Power drink might help you in a wide selection of methods.
Nonetheless, it’s clever to only eat caffeinated products responsibly and avoid caffeine-related
side effects this way. Sports diet firm Optimum
Diet launched Amino Power drink.
Consulting a fitness or nutrition skilled ensures tailored steering for optimum outcomes.
If you drink coffee regularly, you can drink Amino Energy drink with none problems.
This vitality drink has a pleasant style with out the
bitterness of espresso. This article we’ll talk
about these components and how they might help you perform at your peak.
If you want to discover out more about this power drink, this
is the publish for you.
Prospects appreciate the product’s effectiveness and good taste.
Reviewers say it has a pleasant style and is delivered quickly.
Optimum Nutrition is no doubt some of the well-known supplement manufacturers.
The key purpose for this is their iconic Gold Normal whey powder.
But, Optimum Nutrition Amino Energy is getting increasingly more
well-known, as nicely. The coating additionally hinders deposition of undesired byproducts on the particles.
This breaks up the NCM layers, releasing the lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese ions they contain into the answer.
Many say it helps them scale back their espresso intake
and is a superb various to energy drinks. Clients benefit from the dietary supplement’s energy enhance, style, and quality.
They find it helps them focus and keep power all through the day, with a reasonable caffeine level that doesn’t
have an effect on sleep. Nonetheless, some clients acquired a
product without a security seal, which is a concern. This product delivers 14 amino acids in its “Amino Blend” to cease
muscle breakdown, velocity up recovery, and increase muscular efficiency.
Prospects have completely different experiences with the ache stage of the product.
Some discover it helps present energy and feel good whereas working, without causing abdomen upset or gas.
Others report feeling jittery, sweaty, and sick to their stomach after consuming an excessive amount of.
I’ve used Optimum Nutrition Amino Power as each a pre-workout and a noon power booster,
and it has constantly delivered solid results. If you need a pre-workout supplement that supports
energy with out extreme caffeine, this could be an efficient
option.
Clients have completely different views on the dietary complement’s worth for cash.
Some find it reasonable with good components, while others contemplate
it a waste of money and plastic. Complete mix of 5g BCAAs
& EAAs to boost performance and recovery. Optimum Diet is amongst the
main sport nutrition companies in the world and produces the most effective
and the highest-selling protein products within the international market.
If you are sensitive to caffeine, we suggest assessing your tolerance by beginning with 1/2 the instructed serving size.
Signup for weekly provides, complement & training suggestions and extra.PLUS 10% OFF YOUR
FIRST ORDER. We take pride in ensuring our articles are
written by essentially the most knowledgeable and qualified individuals obtainable.
We source and cite our scientific literature from reliable, trustworthy databases.
Caffeine is pretty frequent in candies and plenty of drinks.
That’s why it’s fairly simple to overconsume caffeine with out being fully conscious.
A benefit of Amino Power drink is it incorporates just a few calories and 0g of sugar.
Whereas they’ll offer a fast vitality enhance and assist in muscle restoration, it’s important to contemplate
their general healthiness. The amino acids support muscle operate,
but extreme caffeine can lead to jitters and insomnia.
Customers benefit from the hydration supplied by the dietary supplement.
They find it refreshing and enjoyable to drink, helping them drink
more water. The product accommodates important amino acids and natural caffeine, providing
a sustainable vitality increase within 15 minutes.
Mix up Essential Amino Vitality anytime you want a naturally flavored
increase of power and alertness.
The powder helps them get through their workouts and promotes muscle recovery and development during exercises.
Customers respect the quality of the product, saying it works higher for their bodies than costly pre-workouts.
Optimum Nutrition Amino Energy has an inexpensive price level compared
to other pre-workout choices. One tub of Optimum Nutrition Amino Vitality
(30 servings) costs around $20, which implies that one serving prices round $0.67.
This is a budget-friendly option for many who are looking for a reasonable energy boost and amino acid support.
The drink has very little caffeine and amino acids that the physique wants.
It’s carbonated and caffeinated without any of the unhealthy ingredients found in other
massive name brands. They discover it provides them with the
power they want and helps them stay hydrated.
They discover it dissolves easily, offering a easy enhance without jitters or crashes.
Shaking in a closed container works nicely,
and there is no tingling sensation like another products.
Clients like the standard of the nutritional complement.
ON Amino Vitality is considered one of the finest amino acid supplements, and it’s a reliable possibility
for pre-workout energy and muscle-recovering amino acids.
With a hundred mg of pure caffeine per serving, this complement offers a moderate vitality increase.
Welcome to Costco Food Database, the internet’s #1 resource for all things Costco food.
This firm supplies high-quality sports activities
supplements for athletes and health club rats.
Ultimate Sup stands out as a superb alternative for buying Optimum Diet Amino Energy in Singapore.
One massive egg supplies approximately 0.6 grams of leucine, zero.four grams of isoleucine, and zero.5 grams of valine.
A new strategy for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries is predicated on a hydrometallurgical course of
in neutral answer. The leaching effectivity is improved by a solid-solid reduction mechanism, often known as the battery impact,
in addition to the addition of the amino acid glycine.
They say it has a good taste and works nicely for the worth.
This shoulder and arm workout routine supplies most trainees enough coaching stimulus for optimal training quantity, even should
you only do it as soon as per week. You kick things
off with a combination of compound and isolation workout routines that target all elements of the delts for balanced development.
In this shoulder and arm exercise, you’ll begin with your delts earlier than transferring to your biceps and triceps.
Keep a balanced food plan and stay hydrated to help your body’s restoration and general joint health.
Brachial neuritis may cause inflammation in a bunch of nerves
that service the shoulder and arm, which known as the brachial plexus.
There is usually little ache when you maintain your
arm to your side or lift it to a 90-degree angle.
Wear and tear, and getting older creates worn and roughened
joints over time – surfaces start to rub against
each other, causing popping noises. Following the recommendation of seasoned
shoulder surgeons and bodily therapists throughout
the restoration journey is important to sidestep any setbacks and achieve an optimal consequence.
I proceeded to contact customer service who responded promptly providing to do what they could to repair the issue.
This harm is usually attributable to the eccentric a half
of pulling movements with heavy weight, be it biceps curls or
rows. Weight overload can lead to a lack of control; lifters need to
control the load, not be controlled by it. A lack of management in this space may
cause elbow hyperextension within the concentric part of the motion. A full history
begins with the affected person’s age, dominant hand and sport
or work exercise. It is essential to assess whether the injury prevents or
hampers normal work actions, hobbies and sports. The affected person ought to be
requested about shoulder ache, instability, stiffness, locking, catching and swelling.
Stiffness or lack of movement will be the major symptom in sufferers with adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder),
dislocation or glenohumeral joint arthritis.
The landmine increase is not one thing you wish to load up
the burden and impress your training companion with. This exercise is greatest
reserve for larger rep, decrease weight scheme training.
Begin off with the empty bar and make 5 pounds increments as your power builds.
A good place to start out is between 3-4 units
of reps depending in your shoulder health and the phase of your training cycle
you are in.
Coaching your again is more demanding, and most people will
likely favor to do it when their energy levels are the best.
Nevertheless, if you prioritize your shoulders, be happy to
flip things around and start your exercise with shoulders
as an alternative. One of the benefits of coaching back and shoulders on the identical day is that you could tailor the workout to your
preferences and nonetheless perform your best. Equipment-free shoulder workouts are also typically appropriate for people
of all fitness levels. Under are the 4 of
one of the best alternatives to lateral deltoid shoulder workouts for readers who can’t or favor not to do lateral deltoid exercises.
Follow the five steps beneath to perform lateral raises
with out risking damage. Part of the therapy for shoulder impingement is studying to forestall
future injury.
You can perform it with totally different leg positions (seated, kneeling, standing) and grip
variations (neutral, pronated) to add problem and goal different muscle teams.
This adjustments the angle of the motion and puts more emphasis on the
front deltoids and upper chest. The more upright your torso is,
the extra emphasis you will place on your lateral deltoids instead of in your posterior deltoids.
It is considered one of the best workout routines for constructing shoulder mass and energy, particularly the entrance and facet deltoid muscle tissue.
If you wouldn’t have a fair amount of shoulder mobility, performing these barbell shoulder workouts isn’t recommended.
The Barbell Shrug is amongst the finest shoulder workout routines to build bigger and stronger trap muscle tissue
at residence. It involves lying susceptible on a 45-degree
inclined bench and lifting dumbbells diagonally, offering the
advantages of entrance and lateral raises.
Plus, it’s usually worse at night time, and you might not be succesful of lift your arms above your head or carry things away from your physique.
The ache you’d really feel could be like a toothache, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
That means it might be a radiating discomfort, normally from your outer arm to somewhat beneath the top of your shoulder.
It’s normally made worse when you increase your arms above your head or reach
behind your body, like if you were passing a belt via your belt loops.
Examine out our articles on one of the best cable shoulder exercises or these barbell shoulder exercises.
Even although the traps aren’t your shoulders, they work along with your delts
to improve your performance and aesthetics.
It’s a powerful move that makes use of explosiveness to propel the load upward,
which should enable approximately 30% more weight than a standard shoulder press.
Your shoulder muscles stabilize your shoulder joint and help you transfer your arm in many directions.
Shoulder muscle injuries are frequent in people who use their shoulders
a lot for overhead motions, similar to pitchers or swimmers.
An harm to your rotator cuff, a group of 4 muscle tissue
and tendons that retains your shoulder’s ball joint
centered on its socket joint. Its primary function is to assist initiate actions of bigger muscle tissue, like your deltoids, says Christopher Camp,
M.D., an orthopedic surgeon at the Mayo Clinic.
On one other notice, it forces you to be in a good, stacked position together with
your rib cage aligned pristinely over your pelvis.
Be positive to additionally create relative anterior core and spinal
stiffness, as if you had been in a Plank train. To work around these problems with the machines designed
specifically for shoulder press, I created my very own using
a normal V-squat machine. In either place, perform an isometric maintain for 2-3 seconds at the prime, contracted state.
This combo is a staple movement of our pain-free programming for a
reason, it works! The other side of this equation is that healthy shoulders aren’t built from urgent alone.
This preparation could be the Magellan Shoulder Series I demonstrate on this video.
This collection approaches shoulder integrity from the attitude that scapular movement is the “foundation” of any pressing exercising.
Low reps are a should with the BUP, because the CNS fatigue from the high grip demand is intense.
2-3 units of 3-5 reps appear to work greatest previous
to your restrict presses for the day. What we want is a drill that
gives us the same really feel because the heavy press and the same effort—all without placing the identical pressure on the AC
joint. Fascinating in that I have used it as a one-size-fits-all answer for a selection of problems with the press.
A strain can all of a sudden end result from heavy lifting or an accident, such as a trip or fall.
But it’s additionally an atypical movement pattern, and a
number of the extra cautious lifters worry that it
might harm their shoulders. Fortuitously, there’s no possible method for our
traps to boost our arms out to the sides. That’s part of the motion,
but the main part of the movement is raising our arms
out to the edges, and our facet delts are the one muscle that may do this.
Impingement issues can happen throughout actions that require
extreme overhead arm motion. Seek medical care instantly for irritation within the shoulder
because it might finally result in a more severe harm.
It is a extremely effective train with the added benefit of minimizing decrease again strain. Not Like bent-over barbell rows, the standing barbell
row offers extra rear delt emphasis by permitting you to tug
the barbell again towards your higher chest quite than your lower
ribs. This weblog post will present a complete overview of 75 commonplace shoulder workout routines, using easy names and descriptions.
Use dumbbells heavy enough for no less than six reps and a maximum of twelve.
This is why I like to carry out this movement with a cable machine, and
ideally, a rope attachment, because it allows extra motion and may mitigate any impingement points.
Plus, you might have already done a standing overhead press
with the push press, so it’s good to throw some place selection into the
combination. The overhead press is notoriously difficult due to the biomechanics,
and because of this, many lifters just are inclined to avoid it.
Also, the location, dimension and the severity of your shoulder arthritis.
If your shoulder downside is found early, you can study methods
to reduce pain, change or avoid sure actions and cut back further cartilage damage.
They mention they’re strong and durable, with no points lifting
heavy objects in their store. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that help cushion the tissues round your joints.
Folks with instability might experience ache with shifting their arm
or avoid motions that make the shoulder really feel prefer it desires to slip out of place.
Shoulder accidents are incessantly attributable to athletic activities that involve extreme, repetitive,
overhead movement, corresponding to swimming, tennis, pitching, and weightlifting.
Accidents also can happen throughout on a daily basis household actions such washing walls,
hanging curtains, and gardening.
Returning to the beginning place includes reducing the dumbbells whereas turning your palms
so that they face your physique once more. However, you may require 20 or more weekly sets
if you’re an advanced bodybuilder or lifter.
If that describes you, growing the frequency of your shoulder
and arm workout to twice every week can improve your positive aspects.
The objective of a superset exercise is to maximise the effect of each train and create a greater challenge for muscular tissues.
Furthermore, supersets allow you to perform extra reps in a shorter interval, not
like in traditional sets. Performing shoulder supersets consequently permits your muscle tissue
to work harder and break down quicker. The upright
row is the only open-chain compound exercise targeting the
aspect delts.
It attaches the end of your upper arm bone to your shoulder blade, helping
to safe it in the socket. N some folks, the
acromion forms at a slightly different angle affecting the form of the acromial arch which may cut back the space within the subacromial house.
This also increases the friction on the rotator cuff tendons resulting in shoulder
impingement syndrome. The rotator cuff is a gaggle of muscular
tissues and tendons that encompass the shoulder joint and maintain it in place.
It won’t be sufficient to fully maximize muscle growth, however it must be enough to make progress.
Since you aren’t doing many units, I recommend taking
all of your units of push-ups and lateral raises to failure.
Gains aside, broadening out up high will boost power for your other lifts,
help with stability, and reduce the possibility of harm.
The pec deck rear delt machine fly targets your higher back muscle tissue
and shoulder muscular tissues, significantly the rear
deltoids (backside of your shoulders), Traps, and
rhomboids. The Cable Inside Rotation is a power exercise that targets the rotator cuff muscles and helps to
improve shoulder stability, mobility, and strength. The cable
twisting overhead press is one other effective single-arm cable shoulder exercise.
That means you’ll nonetheless be your strongest when doing delt exercises
even though you’ve already skilled your back.
Examine that to the popular chest+shoulder exercise routine the place your shoulders are heavily concerned when you
practice your chest and tired when it’s time
to hit them. A shoulder superset exercise is a high-intensity routine involving two or more consecutive workouts that activate the
same shoulder muscle groups. Shoulder superset workouts target
the three main muscular tissues of the shoulder—the deltoid, trapezius, and rotator cuff.
First, rotator cuff muscular tissues allow us to maneuver our arms in a round movement, whereas additionally keeping our
shoulder joints secure. Strengthening your rotator cuff muscular tissues by way of specific workout routines helps stabilize your
shoulder joints and facilitates smoother circular arm actions.
Second, trapezius muscular tissues assist our shoulders
and neck, controlling the head and shoulder position, whereas also
helping hold our arms raised.
Your doctor might suggest corticosteroid injections along with
bodily remedy. When you find a grip width and pull peak that works for you, make a remark
of it and keep it up for a minimal of a full coaching phase (3–6 weeks).
Then, offered that you’re being consistent from workout
to exercise, be at liberty to range your approach
from section to phase. When that happens, especially if you’re lifting a heavy barbell, it raises the risk of hurting the
decrease again. It’s fairly a safe carry when accomplished correctly,
but not everyone can do it correctly.
Select your favorites from the record and prepare to witness important improvements in your shoulders’ muscularity and overall posture.
It increases the core-strengthening benefits of a regular
plank by balancing on solely two limbs.
Stability demands enhance when the alternative arm and leg are extended.
“I Might be mendacity if I informed you I wasn’t rattled seeing JuJu mendacity on the ground and crying,” coach Lindsay
Gottlieb mentioned. This is very the case
if you select to pause for a couple of seconds in every rep.
You shall be working towards transferring from a lifeless cease
into the eccentric a part of the movement. An important level will be to
maintain the central nucleus of the body (Core) well contracted and compact to keep away from arching of the again or bad postures.
Anticipate expert-backed workouts, vitamin advice, the newest in power sports, and a complete
lot of motivation heading your means. Brett
Williams, NASM-CPT, PES, a senior editor at Men’s Health, is a certified
coach and former pro football player and tech
reporter.
The ground press was rated as considered one of my high bench press progressions
to take your raise from a beginner to a sophisticated degree.
The ground press is an effective candidate for training lock-out energy as a result of
the elbows are restricted on going beyond 90-degree flexion. As
such, there’s less stress at the degree of the joint that would in any other case be present during a full
vary of movement bench press. For these causes, the ground
press is a very effective train for building tricep muscle mass.
The tricep muscle tissue are most used to increase the elbow within the ultimate lockout portion of
the ground press. Having your toes on the floor will
present extra stability through leg drive. Having your feet straight
ahead will require extra stabilization from you and really
feel more difficult.
They aren’t substitutes for consulting a certified medical professional.
Preserving your arms close to your body is a very secure position in your shoulders since you aren’t inserting them in exterior rotation. This is certainly
the finest option for beginners or anyone with shoulder concerns.
You are pushing the weights away from you primarily using your chest.
Though the pecs are the primary movers in the flooring press, the triceps are additionally extremely important.
You can do that exercise both on a mat someplace in the corner of the gym, or in a squat rack should you don’t have a partner that can help you.
Vidur is an ACE-certified personal trainer, writer, and editor
at FitnessVolt.com.
A bottle of prescription thyroid medication was on the toilet
counter, loose pills unfold across the countertop. Mertz mentioned he was treating a affected person as soon as
with hantavirus at University of New Mexico Hospital.
The patient was sitting on a hospital mattress and began complaining about feeling ill.
The virus is troublesome to detect, as most of the symptoms are akin to the
flu, he said.
This is unlike the bench press and overhead press which may be extra easily translated into sports-specific movements to extend efficiency.
The limited vary of movement, and the reality that
the motion is carried out mendacity down on the floor, signifies that this exercise has restricted transference
into sports. The ability to bounce the weights like you can in a traditional bench
press is non-existent.
Many athletes like to do flooring presses as cross coaching for their sport.
Bodybuilders and anybody else seeking to bulk up rapidly will find
plenty of benefit to utilizing ground presses of their routine.
It’s usually carried out as a show-off transfer, with gym rats competing to see who may do the heaviest bench
press. Ground presses predate the bench press, and when the
bench press rose to popularity, some folks deserted the ground press.
Strive these variations of the kettlebell floor press
to change things up or make the motion tougher.
There are two choices for arm placement in the course of the KB floor press.
You can have your arms at your sides (described above),
or rotate your elbows away from your physique about 45-degrees.
I would not suggest substituting the ground press
with a bench press. Quite, I would use the ground press to enrich
your different pressing actions within your total
coaching program. To ground press, you need a clear gym ground area and tools that
is appropriate for pressing. This could be a barbell but could additionally be a dumbbell or kettlebell.
The ground press is an upper-body urgent motion that mimics a bench press but with a reduced range of movement.
Not only do massive triceps look great, but you’ll also have extra energy and management for a selection of completely different higher body-based workouts.
As a outcome, your triceps will be extra activated on this variation versus the common flooring press.
As you lower the load to your chest, ensure that you thinking about keeping your
chest high (not letting it collapse) and have your elbows barely tucking in entrance of the
barbell. This is particularly important if you have to improve muscle mass for your shoulders and triceps specifically.
Moreover, your chest shall be more energetic if you choose to heave your elbows immediately stacked beneath of the barbell somewhat than have a slight elbow
tuck. There are also loads of variations that you should use to make the
ground press more amenable to your physical abilities.
Developed chest and arm muscle tissue will give you extra management in different athletic activities.
To keep this functionality at a correct stage, it’s potential
to perform particular workouts like cleans, snatches, or plyometrics.
For a meet with weigh-ins the day before, you can cut
a bit more. Most lifters can comfortably get away with a water reduce of ~5% of their body weight, and a few folks cut 10% or
extra.
Performed exactly as anticipated, finishing within a second of my training time.
Join in on a guided exercise, construct your own stack for the day, or go all in on a multi week program.
The sky’s the restrict in relation to designing the blueprint for your objectives.
With no synthetic dyes or coloring, and merchandise
formulated with efficiency in mind, construct your stack
to gas your journey.
If you don’t already eat plenty of carbohydrates, then this won’t work
as effectively but I’m going to imagine that, as a complicated lifter, your food regimen is carb heavy.
Glycogen stores are depleted by lowering your carbohydrate
intake a number of days before completion as your training additionally tapers off.
A 24h weigh in means you could safely lose wherever as a lot as 4%
of your bodyweight beforehand, depending on private tolerance.
No, it’s not definitely worth the risk… especially if you don’t know what you’re doing.
Strongman has a much higher damage fee than Powerlifting
of 5.5 per a thousand hours vs. 1 per one thousand hours of exercise [3].
This is most likely going as a end result of awkward nature of
Strongman, where odd-shaped implements are pressed,
loaded, and carried. Energy sports activities are considered the most secure sports to participate in regarding accidents.
Nonetheless, as a end result of pure one rep energy is extremely
neural, you get a wider vary of physiques and thin athletes you’d never think about putting up big poundages.
Finding a health club that specialises in Strongwoman events and
training is the best probability of giving you the aggressive edge.
The main factor to recollect is that ‘zero-ing’ an occasion is normal and happens to many
strongmen and strongwomen. It doesn’t affect your capability
to participate in the other events and rating well on the events you would
possibly be good at. Getting stronger in the big three will
always help you as you increase your maximum potential
for power. Nonetheless, you can’t rely solely on Powerlifting to make you a great Strongman athlete.
Overhead pressing strength is a must for anyone hoping to obtain success in strongman. Not only are variations
of the overhead necessary to master as a competitor,
however overhead pressing is an amazing method to develop dimension and power in the
upper body, particularly the shoulders. Since strongman allows for lots extra variety than other power sports, it is less probably that you’ll turn into bored by your coaching.
Strongman and Powerlifting are very totally different sports,
although they typically share comparable coaching principles.
Total, in addition to that one decision on the means
to run our lane, the competition was run nicely and the promoters,
volunteers, judges, and everyone else did a fantastic
job. The venue was great, and the events and tools have been solid.
I’d say I suggest the experience, however
USS nats is run by totally different people each year, so this doesn’t necessarily point out how it will go sooner or later.
Our mission is to assist you develop as an athlete,
whether it’s your first time picking up a
barbell or your 10th competition.
70918248
70918248
70918248
70918248
70918248
70918248
70918248
70918248
70918248
It’s a good way to remain motivated and hold
observe of your overall progress. However, alongside these benefits, customers also felt that this wondrous combination factors out the necessity for a strong exercise plan. The mix of Anavar and
Winstrol isn’t meant to replace bodily efforts; it’s there to amplify the advantages of genuine exhausting work, turning common features into extraordinary ones.
Considering a cycle that merges two performance enhancers like Anavar and Winstrol requires a
bit of understanding in regards to the two compounds.
ALL anabolic steroids will shut down testosterone ranges to
totally different extents. How much you’ll be shut you down will differ, relying on which steroid you’re taking.
For example, in my own expertise, something beneath 80mg will NOT lead to important fats loss or energy features.
In my opinion you need this dose or greater to keep away from wasting losing your money.
It’s well-liked amongst bodybuilders as a end result of
anavar’s thought-about a gentle compound.
Although there are several unwanted effects, because it’s not overly powerful or poisonous, most of these unwanted facet effects can often be prevented.
Correct Post-Cycle Remedy (PCT) is essential after a Winstrol and Anavar cycle.
Although AST/ALT enzymes will rise, that is unlikely to trigger any
lasting damage to the liver, as a end result of its self-healing attributes.
Thus, a person is only likely to expertise serious liver
harm if Winstrol is abused and is taken for a quantity of months at a time (without biking off).
If a person is consuming maintenance calories or in a surplus,
Winstrol’s capability to add dimension is extra notable.
Chromium to make you more insulin delicate, Carnitine to help your metabolism,
and various others to help your fats loss endeavors.
The above side effects are particularly widespread when women take different steroids in addition to
Anavar. Subsequently, if somebody needs to realize some muscle, but not
a huge quantity of mass, Anavar will do exactly that.
Anavar’s fat-burning results are considerably completely different to other
steroids, as it also causes a lower in visceral fat
(as well as subcutaneous fat).
The cause why anavar is so effective at growing strength is because of its effect on testosterone ranges, in particular DHT, the most powerful androgen in your body.
As A Outcome Of anavar can build muscle and cut back physique
fat simulatenously, whilst having minimal unwanted side effects; it’s easy to
grasp why gym rats are popping var tablets like they’re candy.
Experts within the fitness and bodybuilding
group usually have diversified opinions on which steroid is better.
Some lean in the path of Anavar for its milder results and decrease risk
of severe side effects, making it a extra sustainable choice for long-term use.
As a gentle anabolic steroid, Anavar does not convert into
estrogen or DHT.
It will amplify the aesthetic effects of Trenbolone (even higher vascularity and definition) while,
on the similar time, you’ll be bulking
up and dropping fats. This is an advanced cycle for users who have already experienced Trenbolone’s harsh unwanted effects.
Tbol is probably considered one of the few steroids
that works equally nicely as a kick-start AAS or one to add to the end of a cycle to complete off
and sharpen your physique, due to its lack of water retention. Turinabol can play a strong
supporting role to boost the effectiveness of
more powerful steroids like Deca-Durabolin and
even simply testosterone itself. Turinabol was first developed in old East Germany and is now
infamous for its use among East German athletes.
It provides nice outcomes with out inflicting any side effects and is highly recommended for individuals who want hard and dry muscles with vascularity.
Nonetheless, it will not be the finest choice for
individuals who are new to using steroids or who’re delicate to its results.
Anavar is much less prone to trigger joint pain, making
it a good selection for individuals with joint issues. On the opposite hand,
Winstrol is more more probably to trigger vascularity and
definition, making it a good selection for bodybuilders and athletes seeking to improve their appearance.
It can elevate levels of cholesterol, increasing the danger of coronary heart disease.
This threat may be reduced by monitoring cholesterol
levels and consuming a nutritious diet. Combining 5 of our most
powerful muscle constructing and fat burning formulas for wonderful,
fast-acting results.
Athletes have been caught using unlawful substances in competitions
to get an unfair benefit. Nonetheless, security risks and ethical questions cannot
be ignored. Begin with lower dosages than talked about and enhance progressively as
wanted. This method, the danger of unwanted effects is minimized and you may see how
your physique responds to the steroids.
WIN-MAX is designed by CrazyBulk as a substitute, combining high quality elements
to help you lose fat and probably even acquire muscle as well.
Nevertheless, if girls take extreme doses for lengthy durations of time,
virilization unwanted effects with Anavar alone are nonetheless potential.
Some women and men who do not want to take steroids, due to their harmful effects, might determine to
take an Anavar-only cycle, solely due to its safety profile.
This diuretic effect can additionally be more doubtless to increase vascularity and muscle striations
whereas contributing to a leaner look. Progestational activity can also be nonexistent in Anavar; due to this fact,
progesterone-induced gynecomastia won’t occur. In medical analysis, the only
incidence of gynecomastia occurring from oxandrolone was in a research
performed on adolescent boys (12). 33 instances of gynecomastia have been reported; however, these findings are contradictory to other research in adults.
Thus, the danger of gynecomastia seems to significantly enhance
if kids utilize Anavar for excessive periods during
puberty. These children were taking moderate doses of Anavar repeatedly for six months to eight years.
The average bodybuilder will run Anavar for a most of eight weeks.
Subsequently, winstrol is rarely utilized throughout bulking cycles,
but remains effective when bodybuilders need to get shredded or are getting ready for a show.
Another purpose why winstrol is utilized in many cutting cycles is as a end result of it’s a ‘dry’ steroid.
We have found this cycle to build similar amounts of muscle to the Winstrol/testosterone cycle,
but with less water weight acquire. Anadrol is very estrogenic, so biking this
steroid in conjunction with a high-sodium food plan is a recipe for water retention and easy muscle
tissue. We find a extra aggressive PCT is needed with this cycle to kickstart natural
testosterone production. The duo of Clomid and HCG has additionally been utilized in research to deal with hypogonadism
by Dr. Michael Scally with success.
This steroid increases energy in both men and women during the slicing the section by serving to the
muscles retain their nitrogen which will be used to produce more energy during
exercises. Winstrol is a well-liked anabolic steroid that’s often utilized by bodybuilders and athletes to boost their performance
and construct muscle mass. It is usually taken orally or injected into the muscles,
and it may be very important observe the dosage directions rigorously to keep away
from any potential unwanted effects. Some frequent unwanted effects of Winstrol embrace zits,
hair loss, and liver injury, so it is very important talk to a healthcare supplier before beginning to use this steroid.
Left unchecked, signs like fatigue/lethargy, low libido, and despair can develop.
Although I make a degree here that an increase in your appetite will benefit many EQ
customers, some people discover it so intense that being hungry dominates your whole day (and night even).
If you’re using EQ whereas chopping, that is going to current vital challenges,
and the fact is that some people can’t use Boldenone on chopping cycles because of
this alone. Anadrol is an oral bulking steroid typically
stacked with EQ for a short portion of the cycle.
EQ is not a giant power booster, so Anadrol takes the
lead and pumps up power positive aspects, whereas EQ
enhances endurance – making for a killer performance combo.
A want to eat more is a giant plus on any bulking cycle (provided you’re filling up with suitable calories).
Oxandrin is still bought at present, but underneath
the current company name Savient. Generic Anavar is now produced and sold,
with the orphan drug designation expiring, dismantling BTG’s monopoly.
Nevertheless, due to this earlier elevation in price, along with excessive demand for Anavar and just a few labs on the planet producing it, Anavar nonetheless remains costly today.
We comprehend it to be the highest-priced pharmaceutical steroid, together with Primobolan. Anavar
was also prescribed for treating osteoporosis
because of its ability to extend bone mineral density. These varied forms of testosterone possess distinct esters, which
decide their absorption fee and duration of presence within the physique.
Food Plan and current physique weight will determine how
far your fat loss can go, but a 5lbs lack of fats over a cycle when you’re already
lean will enhance the physique. 20-30mg is a safe start line for first-time Anavar users who are nervous about side effects.
While this is a good dosage range if it’s your first time using Anavar, some
guys won’t see a lot of response at this degree.
As all the time, flexibility in adjusting your dose during the cycle is required.
Since Anavar begins working rapidly, you’ll have a good suggestion of whether you’re responding to this low
dose early.
Testosterone replacement therapy is a type of hormone remedy by which the primary objective is to offer testosterone as a
medicine, usually for males with abnormally
low levels. The goal of TRT is to counteract any lower
in regular testosterone production. We have discovered this cycle
to build related amounts of muscle to the Winstrol/testosterone cycle, but with
much less water weight acquire. In our expertise, Winstrol and trenbolone cycles are highly toxic AAS and solely
appropriate for advanced steroid customers. The under Winstrol
cycle is perfect for somebody who’s already taken Winstrol or milder steroids, corresponding
to testosterone or Anavar. This supplement’s formula makes certain that your testosterone levels are skyrocketing whereas in your exercises and boosting the manufacturing of luteinizing hormone.
Throughout the cutting and weight-reduction plan section, Winstrol will
cleared the path with its intense shredding outcomes.
I would use it both the final four weeks of the cycle
or in the center when your lifts stall to offer slightly additional assist.
SARMs are a more modern growth on the earth of performance-enhancing drugs,
and so they offer many of the similar advantages as Anavar with out some of the
negative unwanted side effects. SARMs is not going to improve DHT levels to the same and, subsequently, won’t be as
powerful. SARMs had been then developed to exchange these Steroids after even essentially the most
refined steroids (Anavar and Primo) nonetheless had severe unwanted
effects. The purpose is simply the reality that Anavar is
stronger – plain and easy.
This dynamic duo of steroids is a well-liked alternative
among bodybuilders and athletes alike, known for its capacity to construct
lean muscle mass, enhance strength, and enhance overall efficiency.
When contemplating whether or not to stack Anavar with SARMs, it’s essential to understand the advantages and potential dangers concerned.
Stacking means utilizing two or more performance-enhancing compounds concurrently
to achieve desired outcomes, similar to improved muscle progress or fats loss.
Another quite common effect is acne due to the elevated oil that is going into your system.
Male sample baldness is another unwanted effect of taking artificial testosterone.
Proviron isn’t going to dry you out to the extent that something like Masteron does.
Still, it’s also one of the safest AAS to make use of, and even when used as the only hardening agent,
it may find yourself in a wonderful aesthetic look and may achieve this very quickly.
Sure, the potent libido boost can additionally be tremendous, and Proviron is a wonderful “happy steroid” that
you’ll really feel good on.
Right Here, I need to share just some of the experiences and
outcomes that guys are seeing with Clen –
whether or not they’re using it on its own or stacked with different PEDs.
Clenbuterol’s half-life is estimated to be anyplace from 35 to 48 hours.
This makes it lively throughout the day and evening,
regardless of what time you are taking it. This can current
some points for Clen users – as a result of this drug is well-known for causing sleep points.
Clenbuterol has been round because the Seventies,
though it’s solely lately become a extensively known name in performance circles.
The primary medical objective of Clenbuterol is its use as a therapy
for asthmatics, the place it helps open the airways and assist breathing6.
Although these are the commonest steroids used by beginners (due to their delicate nature),
they’re still illegal and might trigger severe unwanted aspect effects.
Thus, no anabolic steroid is “100% safe”, regardless of what any juiced-up bodybuilder may tell
you. Most Likely essentially the most extreme unwanted
aspect effects of Proviron concern cardiovascular health18.
Cholesterol changes can be severe for some customers, whereas others won’t see
any changes (you will need bloodwork to confirm).
We discover a more aggressive PCT is required with this cycle to kickstart pure testosterone manufacturing.
The duo of Clomid and HCG has also been utilized in research to treat hypogonadism by Dr.
Michael Scally with success. Nolvadex is a SERM used to deal with low testosterone levels
post-cycle (4). This has helped our patients’ hormonal profiles return to regular ranges inside a number of weeks of cycle
cessation, which in any other case can take several months.
Boldenone is interesting in its mechanism to increase Purple Blood Cell Count and Hematocrit ranges.
This will massively drive up the body’s capacity to hold oxygen, that means it is a pretty good option for
individuals who do a ton of quantity when coaching.
Testosterone Enanthate continues to be a favourite for TRT with many males,
but then there is a giant cohort who swear by Sustanon and won’t use anything.
The difference in opinion could come right down to how individuals administer it – particularly, how usually.
With Out shorter interval injections (no more than 5 days apart),
you may get further estrogen-related unwanted aspect effects showing with
Sustanon, even at low TRT doses. Testosterone itself increases the muscular energy of the male physique, and with a better dose comes
a higher level of muscle strength. Although Sustanon 250 isn’t what we’d name
a strength-boosting monster, you’ll notice a big enchancment
and find it easier to lift heavier weights and push via
longer and harder sets. Apart From the Propionate ester,
the other three are not used or obtainable as standalone testosterone esters as they have been developed
for this combined formulation. Like all testosterone steroids, Sustanon 250
is flexible, can be run independently or stacked with different AAS, and can be used in several
steroid cycles.
When it involves enhancing athletic efficiency and muscle
progress, the mix of Anavar and HGH has become increasingly
in style among bodybuilders and athletes. Whereas this stack can provide impressive results
in the quick time period, it’s important to think about the potential long-term well being impacts.
It’s necessary to notice that these are basic
recommendations, and particular person elements similar to age, fitness objectives, and general health must be considered.
Moreover, correct medical supervision and guidance from a qualified
healthcare skilled or experienced bodybuilder are important when endeavor any anabolic steroid cycle.
Testosterone, a hormone that is produced naturally in the physique, plays a pivotal position in muscle development,
power, and general well-being. Test types the foundation of the Check and Anavar
cycle, setting the stage for appreciable features in muscle mass and power.
Anavar is a relatively mild steroid, in comparability with different AAS corresponding to trenbolone or anadrol.
Nevertheless, anavar’s a banned substance and is against the law to purchase in many nations – without a prescription (including US and UK).
Some people say they don’t discover a lot on anavar, which I put down to a too-low dose.
Nevertheless, the people who mentioned it DOES work for them additionally said their gains are dose-dependent (which is what I
find). These like Lee Priest or outspoken bodybuilder
‘Aarron Lambo’ who aren’t afraid to speak up and
reveal a few of the darker secrets of the bodybuilding world.
Though there are genetic limitations and
not everybody experiences plenty of vascularity, anavar drastically improves your
chances of having veins piercing by way of
your your biceps. This is as a end result of anavar reduces the fats which is
overlaying your veins, and it fills your muscular tissues with more glycogen, giving them
more fullness.
On the opposite hand, TRT entails the administration of exogenous testosterone to restore hormone levels in individuals with low
testosterone. Like the gents, feminine Anavar users’ cycles
typically span six to eight weeks. This time-frame permits for important enhancements in muscle
tone, vascularity, or power with out pushing the physique into a hazard zone of prolonged publicity
to the compound. In case of stacking, women can take into consideration teaming up Anavar with different delicate
steroids, maintaining the dosage low. This method ensures
harmony between compounds and maximizes the potential of their bodybuilding quest.
Oxandrolone just isn’t an especially potent androgenic steroid, but androgenic exercise
does exist. Such activity can result in acne, accelerated hair loss in those predisposed to male sample baldness and
physique hair development.
The dosages for Anavar differ for men and women, so it’s important to understand what the really helpful doses are for each.
Nevertheless, the acquisition of anabolic steroids is a prohibited
exercise that entails quite a few additional drawbacks.
These embody Anavar dietary supplements being counterfeited,
underdosed, or contaminated with dangerous substances (4).
In the worst cases, some guys will flip to medicines or different sleeping
aids to deal with this problem as a result of if you’re not
sleeping properly, your outcomes and performance are in jeopardy.
It comes with a spread of extra potential unwanted facet effects that not many different steroids will trigger, no less than not to the
extent that these opposed effects can current themselves with
Tren. A post-cycle therapy plan is essential after using Parabolan as it’s going to bring about a minimum of a reasonable suppression of testosterone.
Nonetheless, in many instances, it is going to be excessive or total suppression or shutdown. And if you’re stacking Tren Hex with some other suppressive
compound, this impact will be amplified.
Still, when users devour Anavar’s high dose and use it for the lengthy run, it
might cause varied antagonistic unwanted effects that affect the user’s health.
Moreover, TRT can enhance the anabolic effects of Anavar by offering a
stable foundation of testosterone to help muscle
progress and restoration. This may help to maximize the benefits of Anavar, corresponding to increased muscle mass, strength, and fat loss.
This intermediate Anavar cycle introduces Testosterone run at a TRT (Testosterone Replacement
Therapy) dose of 100mg weekly, simply to maintain normal physiological operate.
Trenbolone has a massive status amongst bodybuilders as the ultimate
word anabolic steroid, but its historical past is comparatively unremarkable
in comparability with many different AAS.
Three different esters have been developed, however none are used for human well being at
present. Only one of the esters (Trenbolone Hexahydrobenzylcarbonate) was approved for human medical use for a short time.
HGH is a subcutaneous injection rather than an intramuscular injection like anabolic steroids.
This makes it simpler to inject for most individuals as you
aren’t putting a needle into a tough muscle, which may be painful.
If you’re on the lookout for huge gains in lean muscle tissue in a relatively
short period of time, you’ll be disenchanted in this steroid.
Many tend to assume the aim of anabolic steroid use is to advertise large gains in muscle tissue,
and if this doesn’t occur you’re supplementing for the incorrect reasons or the wrong
means. What many fail to understand is that positive aspects aren’t defined
as mass gains and nothing else, many supplement for total body transformations that might not embody large buildups
in mass.
It implies that its molecular makeup won’t change as it goes through the liver.
Most of the steroids usually have their compositions changed as they
cross by way of the liver. But with Anavar, it reaches the bloodstream and
it reaches the cells when it is nonetheless intact. Due to this, some customers could
expertise unwanted effects similar to hair loss for many who are susceptible to
male baldness.
Nonetheless, this is not beneficial because of excessive hepatic and renal toxicity.
Although Anavar just isn’t the most potent anabolic steroid, it
nonetheless has a notable impact on lean muscle mass.
In scientific settings, even sedentary men have
experienced constructive modifications. Sadly, many steroids are counterfeited on the black market; subsequently, it
is unimaginable to know what the compound is
with out testing it. Nonetheless, in practice, we discover girls
experience multiple indicators of clinically low
testosterone levels following anabolic steroid use.
This trio of steroids should be thought-about somewhat harmful,
even for experienced bodybuilders, and must be
used sparingly (if at all). If somebody has taken testosterone before but not Anadrol, this cycle will additional improve muscular power and hypertrophy.
Nonetheless, Anavar is metabolized in another way than other
oral steroids, with the kidneys taking over more of the
workload, and thus it causes much less hepatic inflammation. Those wanting to protect their hair follicles could
take DHT-blocking supplements.
These long-term unwanted side effects are much more likely
to come about from any other more highly effective steroids you could be stacking Anavar with somewhat than from Anavar itself.
Females can acquire strength and lean gains at low doses, and stacking
Anavar with another type of compound called Ostarine (a
SARM) can result in outstanding results with minimal unwanted
effects. At a minimal, all male users will need to stack Anavar with testosterone at a base TRT dosage to keep
away from the results of low testosterone on account of Anavar’s suppressive activity.
If Anavar is getting used as part of an extended contest prep cycle, it will often be saved for the ultimate weeks of the cycle to
get you as lean and shredded as potential.
The Anavar/Clen combo is sweet sufficient to get you some
spectacular weight reduction results. Hold Clenbuterol to 50mcg daily and run it in 2 weeks on/2 weeks off pattern. Here is a solid Anavar slicing stack that features Clenbuterol and HGH.
On the draw back for Masteron, it dries out the joints and may trigger joint ache, whereas Anavar can be joint supportive to a
degree. Anavar has a benefit right here and can even have a extra optimistic effect on your tendons and joints.
Once again, in case you are delicate or don’t wish to danger it,
stick to the beginner plans listed above. You’ll also wish to contemplate the time of
day – some folks find sleep points develop with Anavar29, so the means in which to attenuate impacts on your sleep is to
take Anavar within the morning. Customers expertise decreased
appetite when utilizing Winstrol due to its capability to destroy subcutaneous fat cells.
Anavar just isn’t the most suppressive steroid, but your natural testosterone production is
prone to have taken successful. This may cause symptoms of low testosterone
when your cycle ends, including loss of muscle and fats achieve.
If you have not any current kidney issues, using low
doses and short cycles of Anavar is unlikely to trigger kidney injury.
Nonetheless, if you use extreme doses and long cycles, you’ll be putting your kidneys – and other organs – at nice
threat of harm.
This is why Trenbolone seems to excel so much more than different anabolic steroids in a calorie deficit.
Whereas that might be a compound ideal for somebody in search of maximum hypertrophy with a relative
lack of androgenic unwanted effects like hair loss, on this situation the alternative
is what we’d be shooting for. When it comes to nitrogen retention, we’ve
seen in clinical research that there’s not a major difference between essentially the most
potent steroids from every category of the anabolic steroid household
tree.
In other words, it may possibly slow down and even shut down natural testosterone production in your physique,
and thus, it’s crucial that you just begin a PCT as soon as your Dianabol cycle ends.
Initially, whenever you take Dianabol, your physique goes to
experience a spike in testosterone ranges. However, in the later phases of the cycle,
Dianabol is going to suppress endogenous testosterone manufacturing in your
body. When there might be too much exogenous
testosterone in the bloodstream your brain signals the physique to decrease and
even shut down its own testosterone production. A supplement may
say that it has a recommended dose of 6mg-12mg of Testosterone (or
some other supplement) for those on a normal-weight coaching protocol.
This is a traditional dose range, and it’s generally recognized that this dose amount is not required when making an attempt to build muscle mass.
Dianabol works by binding to the androgen receptor,
which in turn causes a rise in testosterone
manufacturing. While Turinabol can provide some mass gains with out fluid
retention, it’s not considered a bulking steroid.
It won’t have you gaining muscle like actually highly effective anabolic steroids can,
and this is not the aim the majority of folks use for it.
Turinabol is greatest thought-about a performance-enhancing
compound rather than a bulking steroid. After a cycle of Dianabol (methandienone), an oral anabolic steroid, your
physique needs time to recover and restore its natural testosterone
manufacturing. PCT is a crucial step in managing the potential unwanted effects of
suppressed testosterone levels and helping your
physique return to its regular hormonal stability.
Anavar, also called oxandrolone, is another synthetic anabolic steroid generally used in bodybuilding to promote muscle development and fats loss, as well as
to improve energy and endurance. Anavar works by increasing protein synthesis, similar to Dianabol, however it’s considered
to be a milder steroid with fewer unwanted aspect effects. However, Anavar can nonetheless trigger potential dangers similar to liver
toxicity and decreased testosterone levels. When considering the use of any anabolic steroid, it is
important to bear in mind of potential unwanted
aspect effects and dangers. Dianabol carries a higher
threat of estrogenic side effects because of its conversion to estrogen within the body.
This can lead to water retention, bloating, and the development
of gynecomastia (enlargement of male breast tissue).
Yet, we’re conscious that small doses (12.5 mg daily)
have minimal effects on liver enzymes. On the other
hand, higher doses might cause vital hepatotoxicity, even in in any other case healthy bodybuilders.
Anavar and Winstrol are similar in a lot of methods, but
Anavar is the better choice for slicing.
These three compounds are characterised primarily by their broad spectrum effects on anabolic and androgenic dependent
capabilities, in addition to their interplay with aromatase.
This article will serve as an overarching introduction to
how every category can be leveraged within the anabolic steroid
household tree, in addition to the final strategy I would
take towards compound selection. Since Dianabol is an oral steroid, it may possibly put a strain in your liver.
HDL will often be lowered, though hardly ever considerably enough to trigger long-term issues.
The real threat is if you stack Proviron with other cholesterol-raising steroids, the place this side effect worsens.
On the upside, it reveals no estrogenic results and can act as an anti-estrogenic to help combat gyno.
Whereas this isn’t anyplace near as powerful as a real aromatase inhibitor, it is a welcome attribute of
a steroid when so many different steroids show the very reverse results.
Nonetheless, while estrogen-related side effects aren’t a difficulty
with Proviron itself, there are other potential
unwanted effects to be aware of. The fact is that
efficiency customers will almost all the time
be stacking Proviron with a quantity of other suppressive steroids, so PCT
will have to be deliberate based on the other
compounds you’re utilizing.
Even although Proviron is an oral steroid, it doesn’t trigger
injury to the liver, which is another reason this steroid is considered one of the least
dangerous. In abstract, Anavar (Oxandrolone) is a
mild, efficient steroid with a well-regarded security profile.
Developed by Searle Laboratories, it presents muscle-building advantages with fewer side effects,
making it a popular alternative among many athletes and bodybuilders.
Anavar, additionally known by its chemical name Oxandrolone,
is one other well-liked anabolic steroid. Like Turinabol, it was developed within the 1960s, however this time by Searle Laboratories, a pharmaceutical firm that later turned a
half of Pfizer.
By combining these two steroids, you probably can create a robust
fat-burning cycle that may help you to realize a lean, ripped physique.
Anadrole re-creates the results of Oxymethalone (known as Anadrol,
one of the highly effective anabolic steroids in existence) however without the unwanted effects.
Yohimbine works by blocking alpha-2 adrenergic receptors
positioned in cussed fat shops.
For the feminine athlete, adding Anavar may be helpful at any time and for any cycle, from bulking to chopping.
Hi, I’m Dr. Grant Fourie, a devoted medical professional enthusiastic about advancing healthcare in our community.
With 20+ years’ of medical background, I try to supply compassionate and revolutionary care to my sufferers.
Outdoors the clinic, I enjoy sport and health hobbies,
which maintain me balanced and impressed. In the United States, the average retail value for Oxandrolone is round $4-5 per 2.5mg pill from approved pharmacies with a sound prescription.
Though Winstrol could have an edge on enhancing physique composition, its unwanted side effects are dramatically
worse in comparability with Anavar. Winstrol certainly isn’t protected
and isn’t suitable for novices, whereas Anavar is
commonly taken as a primary time cycle. This is due to Winstrol growing free testosterone, with it strongly binding to SHBG (sex hormone-binding globulin).
Nonetheless, the thing with Proviron is that not everybody uses it for hardening results.
Some (perhaps a lot) men are using Mesterolone for the feel-good issue
– both the mental advantages (feeling extra assured and pleased, for example)
and, after all, the big enhance in libido. As one of its previous medical uses, it’s not surprising that Proviron can improve male fertility
by enhancing sperm count14. Though unlikely to be a purpose most of us are utilizing
it, it’s a pleasant bonus profit that actually can’t
hurt.
The best method to make use of Anavar is to start with
lower dosages, and to increase over the course of eight weeks,
where males must be beginning with 20mg per day,
and girls from 2.5mg per day. Understanding how Oxandrolone cycles differ by method of user expertise is integral to selling correct usage and mitigating potential complications.
A user is typically classified as a beginner or an advanced user,
with each category warranting distinctive cycle duration and dosage considerations.
An Anavar cycle typically ranges from 4 to 6 weeks for newbies, while extra seasoned
users may extend the interval to eight weeks. It’s crucial
to notice that Oxandrolone is administered in a controlled method.
Extended usage beyond the advisable limit can pressure the
liver and result in adverse health outcomes.
A few of our sufferers have skilled insomnia or problem sleeping on anabolic steroids, together with Anavar.
This can persist for the primary few weeks of a cycle, after which sleep patterns
typically enhance. However, if a person stacks Anavar with different anabolic steroids, this suppressing
effect will be exacerbated. Alternatively, if a user does not desire to wait
several months, they will incorporate post-cycle therapy to reduce back this recovery time period.
Nevertheless, the reality is slightly different…
Mesterolone didn’t exist till the Nineteen Sixties.
Schering was (and nonetheless is, beneath its new owner, Bayer)
the corporate that introduced it for medical use in 1967.
You know, I wouldn’t advocate using both of those steroids, to be trustworthy.
I cycle on and off for a couple of years, and I’ve seen lots of people get messed
up from utilizing them.
The solely drawback with this cycle is that will most likely
be harsh on the body. Our LFTs (liver function tests) clearly show Winstrol and Anadrol to be hepatotoxic steroids.
These are additionally very suppressive compounds in regard to testosterone, and they will have a deleterious effect on the center,
with elevated LDL and lowered HDL cholesterol
scores. Nonetheless, when Anadrol isn’t used along side a high-calorie food regimen (with
a lot of sodium), water retention is minimal. If somebody has beforehand
used Anadrol and their body’s tailored to this compound, they may cycle it again, however at a higher dose
and for an extended time period (for elevated gains).
As A End Result Of it contains some very fast-acting esters, Sustanon 250
kicks in quickly firstly of the cycle, so you’ll
begin seeing improvements in endurance and power after only a few days.
Nonetheless, there are research suggesting clenbuterol has muscle-building effects in animals (32).
Clenbuterol’s anabolic potential stays controversial, with our
sufferers and many bodybuilders failing
to expertise any notable will increase in muscle hypertrophy during sensible
settings. This is due to them being fat-soluble compounds, thus causing the steroid
to dissolve when taken with dietary fats. Therefore, Anavar and different anabolic steroids
should be taken on an empty abdomen for optimal results.
Nonetheless, we all know of bodybuilders which have retained just about all of their outcomes on Anavar when they continue common weight
training. Such successful muscle retention could additionally be
attributed to Anavar not aggressively shutting down endogenous testosterone
manufacturing. The primary purpose of post-cycle remedy is to restart
endogenous testosterone production.
This can additionally be why powerlifters usually administer
Anavar previous to a competition for maximum energy with
out vital weight achieve. Anavar and all anabolic steroids
are essentially forms of exogenous testosterone; thus, Anavar will improve muscle mass.
In distinction to anabolic steroids, a woman’s
dose of clenbuterol is often much like a man’s. Intermediate bodybuilders who’ve previously used
steroids and have adequately tolerated testosterone and Anavar
in standalone cycles sometimes administer the aforementioned protocol.
Finest of all, Trenorol is completely protected and authorized,
so you must use it without worry. Whether Or Not you’re a bodybuilder,
powerlifter, or just trying to get ripped, Trenorol is the
proper complement for you. If you’re seeking to get jacked, there’s no higher method to do
it than with Trenorol. This authorized different to the banned steroid Trenbolone is ideal for anyone
who needs to bulk up rapidly and efficiently.
For these seeking much more extended motion from their steroids, Parabolan or Tren-hex is another choice that offers a 14-day half-life.
Many customers report softer erections or the lack to
climax while on cycle.
Obtaining it from an underground lab can be off-limits
and no form of Trenbolone has received approval for human clinical use.
Subsequently, it goes with out saying that Trenbolone shouldn’t be
considered an choice for feminine bodybuilders or another sort of consumer.
Use of this hormone can result in numerous male traits shortly developing, similar
to facial hair, a deep voice, broad shoulders and even a male-like jawline.
Temper disturbances corresponding to irritability,
despair and aggression have been linked to taking this
drug. Whereas for some males this might be a trigger for concern, these determined to
look as muscular as possible will not be overly anxious about dropping a few locks if it means attaining their fitness goals.
With more pure options now available, there’s no have to danger disqualification when competing.
The general affect of Trenbolone on ldl cholesterol must
be less significant than most oral steroids, however it’ll normally be much more important than most injectable steroids.
If you have high ldl cholesterol you ought to not supplement
with this anabolic steroid. If you’re wholesome sufficient for use, you’ll want to
ensure you defend your ldl cholesterol via food regimen and
exercise. The diet must be rich in omega fatty acids, low in easy
sugars and saturated fats with every day fish oil supplementation being strongly
beneficial.
To help you make an informed decision, we have created a desk
evaluating the differences between these two steroids.
The optimum dosage of the Sustanon Trenbolone cycle is a subject that requires a comprehensive understanding of the
underlying science. Sustanon is a mixture of testosterone esters
that work together to provide a sustained launch of testosterone into the physique.
This permits for an extended anabolic impact and helps keep secure hormone levels.
It additionally has the potential to assist in fat loss,
making it a beautiful option for these looking to achieve a lean physique.
Trenbolone is known for its severe unwanted facet effects, corresponding to insomnia, cardiovascular strain, and potential psychological
health impacts like anxiety and aggression. It just isn’t approved
for human use, and its legality is restricted in lots
of countries. This article explores 10 execs and 10 cons of Trenbolone, offering insights into the advantages and challenges of its use.
The value of the raw powder to manufacture is far more than that of testosterone or deca.
The preliminary spike happens very quickly with a quick decline of blood ranges over
a 24 – seventy two hour period. Most customers will inject Tren Ace
3x weekly to keep ranges secure and optimum. In common,
Trenbolone Enanthate is what could be considered the superior Trenbolone user’s
Trenbolone.
It also increases your energy and endurance, permitting you to push your exercises to the following
stage. Trenbolone acetate is no doubt one of the most
revered and efficient compounds in relation to cutting.
Trenabol, also called Tren Enanthate, is a derivative of the anabolic-androgenic steroid nandrolone.
Keep In Mind that the influence of steroids on erectile well being can range
from person to person, and not everybody will expertise
ED as a facet effect. Everyones favorite psychological catastrophe in a bottle, grab your popcorn and load
up your bitcoin. Everyones least favorite compound by week 8+ and their
favorite compound after they arent on it, lets see who actually will publish pics justifying their tren dosages.
Such results, spoken of a lot many assume that if you do not experience such effects
the trenbolone isn’t actual.
As a man myself, I can attest to the fact that steroids could cause you to develop a
deeper voice. This is as a end result of steroids increase testosterone levels, which results in the event of
male traits, corresponding to a deep voice. In this weblog submit, we are going to
talk about 12 of the commonest trenbolone unwanted facet effects
and how to keep away from them. If you’re planning on using
trenbolone, you will need to concentrate on these potential side effects and take steps to forestall them from happening.
The threat of gynecomastia must be thought-about low, as
neither Deca nor tren raise estrogen levels notably. Nonetheless, gynecomastia
remains to be attainable on every of those anabolic steroids by way of totally different hormonal shifts.
Deca isn’t androgenic as compared, so we find it to be one of the
optimal anabolic steroids for inhibiting DHT (dihydrotestosterone) ranges and maintaining hair
follicles intact. For chopping cycles, Tren Ace, for
example, is often stacked with Testosterone Propionate
for an 8 – 10 week cycle.
Finally, there are both advantages and drawbacks
to each, which will be addressed shortly. Trenbolone Enanthate when it comes to launch price and pharmacokinetics is
actually similar to Testosterone Enanthate (or any anabolic steroid affixed with the Enanthate ester).
Because the half-life of Trenbolone Enanthate is kind of near Parabolan (Trenbolone Hex), the 2 are simply
interchangeable with each other. Numerous anabolic steroids have unfavourable traits, such as
excessive aromatisation levels. Trenbolone, in distinction, doesn’t obtain this, which is one of its benefits.
Oestrogen encourages the expansion of fats cells, which results in bigger male breasts
and extra physique fat.
The ester itself doesn’t have an result on Masteron’s activity because it becomes hooked up
over time as soon as you’ve administered the steroid, leaving Masteron to take full effect.
Enanthate is tougher to search out, although it comes with the benefit of fewer regular injections because
of its longer half-life. The worst half about steroids isn’t
just the unwanted effects, but it’s the addiction that results in your demise.
Early detection of issues permits customers to take motion, whether by decreasing the dose, pausing the cycle, or looking for medical
assist. In a steroid cycle, dosage refers to how much of a drug is taken in a given time
period, usually measured weekly. A “cycle” usually lasts wherever from 6
to 12 weeks, depending on a person’s expertise
and objectives.
Most steroids share an identical side effect profile, however Trenbolone is
a little bit of an outlier. 400mg weekly of Equipoise and 350mg weekly
of Tren Hex will take you thru 14 weeks with these longer-acting steroids.
Testosterone enanthate is used solely to supply a base stage of testosterone, and 100mg is
sufficient for this objective. Most users won’t want to go beyond this already
high dosage of Tren, but when you’re hardcore sufficient and tolerating the side effects, you presumably can step as much as a extra superior cycle.
An intermediate cycle may include an extra compound, on this case, Dianabol, to provide the cycle a mega kick start.
An instance of a female operating a Tren Ace cycle will contain these wanting to organize for physique modeling
competitions. Doses might be very low in comparison with males –
under 30mg per week most, however as little
as 5mg if it’s your first try.
These studies usually concentrate on understanding the compound’s mechanism of action,
which might doubtlessly lead to the event of safer, extra targeted anabolic therapies in the future.
Nevertheless, such analysis is carried out under strict ethical tips and doesn’t involve administering Trenbolone to human subjects.
The lack of human medical makes use of for Trenbolone is also
because of ethical and safety considerations.
The compound’s highly effective results on the
physique’s hormonal techniques make it difficult to use safely in a medical context.
The potential for abuse and the issue in controlling its effects make
it unsuitable for many medical purposes. Moreover, the
long-term results of Trenbolone use in humans usually are not well-studied,
further limiting its potential for medical use.
I’m not saying it’s something you can’t control, but it was
there for me each time I had ever used it. Trenbolone acetate (Tren Ace) is absolutely the
most bang in your buck you can see on the planet of steroids.
The severity and prevalence of unwanted aspect effects varies
relying on dosage, length of use and other particular person components.
There’s additionally analysis on Australian males highlighting unwanted
side effects like aggression, violent behaviour, and impulsivity regulation issues, and the
influence Tren can have on mental health and relationships.
The product’s user-friendly dosage format and accessibility are key points of interest.
Bear In Mind, skilled recommendations and ideas can present priceless guidance, but every particular
person is exclusive. Pay Attention to your physique, make
changes as wanted, and search skilled advice when needed.
With the best strategy and accountable utilization, Trenbolone
could be a useful device in attaining your fitness objectives.
It additionally leaves the physique sooner than the long-acting Tren enanthate, with a cycle lasting anyplace from 8-16 weeks earlier than it has completed
its potent course. Trenbolone has been linked to elevated
ldl cholesterol and blood strain levels in some customers, which may lead
to critical cardiovascular ailments if left unchecked.
This is a really controllable dose for most men, ought to be very
snug, and should present fantastic results. Each day can be fantastic however
won’t really provide a lot of a benefit over each different
day. Nevertheless, it is potential to only inject the hormone
on a regular three day every week schedule, corresponding to every Monday, Wednesday and Friday.
This will cause a slight dip in blood levels with the two days in a row of no administration,
but, outdoors of competition circles, it actually shouldn’t be an enormous deal and even noticeable.
Like all forms of Tren, excessive doses of Tren-Hex
aren’t required because of the reality this is such a strong steroid (five occasions as highly effective
as testosterone). Tren Hex is great for bulking, strength, and
lean mass gains but is also powerful for cutting and fats loss.
Some customers also incorporate over-the-counter supplements into their PCT routine.
These might embrace ingredients like D-Aspartic Acid, which may help stimulate LH manufacturing,
or Tribulus Terrestris, which is believed to support total hormone health.
Nevertheless, it’s important to notice that the effectiveness of these dietary supplements is often debated,
and they should not be relied upon as the primary methodology of PCT.
While Trenbolone is broadly recognized for its use in bodybuilding
and athletics, its medical applications are limited and primarily confined to veterinary medication. Understanding the medical context of Trenbolone is essential for appreciating its potent results and the reasons behind its restricted use in human drugs.
Some of those trenbolone cycles are extraordinarily harsh, and we have
found them to be very damaging to the physique (at least in the quick term).
If you endure from these results using compounds similar to Cabergoline
might help to reduce and stop them. As with anything to do with performance-enhancing drugs, not every little thing works for everybody.
Trenbolone acetate, generally known as ‘Tren A’ or ‘Tren Ace’ is known as the ‘King of steroids’ for a cause.
I just really feel that ancillaries like cabergoline should have been talked about, as prolactin/progesterone gyno
and Tren dick are very actual. Not many individuals haven’t any
sides, and if taking with Check, that the appropriate amount of AI is taken as nicely to control E2.
Given Trenbolone’s long-lasting results, particularly with longer-acting esters like Trenbolone Enanthate, PCT usually begins 2-3 weeks after the final injection. This allows time
for the Trenbolone to clear the system before starting PCT.
For shorter-acting esters like Trenbolone Acetate, PCT might start barely sooner, round 5-7 days
after the last injection. Long-term use of Trenbolone can doubtlessly lead to more extreme health points.
These can embody kidney injury, particularly in these predisposed to kidney issues.
This means you may bounce again quicker after intense coaching sessions, able to hit the ground operating for the following one.
Enhanced athletic performance is another generally reported
benefit, with users experiencing increased energy and stamina.
Options include other anabolic steroids like testosterone or Nandrolone, authorized dietary supplements
like creatine and protein, and natural methods corresponding to
optimized food regimen and training.
Familiarizing yourself with the current authorized standing of Trenbolone in your space is crucial for making knowledgeable decisions and avoiding authorized issues.
Before embarking on the journey of acquiring Trenbolone, it’s
essential to listen to the authorized concerns surrounding its purchase and usage.
The legal standing of Trenbolone can vary from country to nation, and even inside regions of a rustic.
Researching and familiarizing your self with the current authorized standing of Trenbolone will assist
you to make knowledgeable decisions and ensure compliance with the law.
The beneficial dosage and cycle size for Enanthate
can range relying on components corresponding to experience degree and desired results.
Once certain to the androgen receptors, Trenbolone stimulates anabolic processes corresponding to protein synthesis and nitrogen retention. This results in a rise in muscle mass and power,
making it highly wanted by athletes and bodybuilders. Trenbolone additionally has a pronounced
effect on enhancing the body’s metabolic fee, leading to elevated fats
burning and improved physique composition.
Therefore, it could be very important seek the guidance of with your doctor regarding the suitable dosage for this
specific cycle. This drug can only be used by men, as virilization and
virilization can occur when even the smallest dose is taken by women.
It is a spinoff of Nandrolone, nevertheless, its effects are considerably different from this steroid.
Many users report experiencing “Tren cough,” which is a sudden fit of coughing that occurs shortly after injecting Trenbolone.
Kidneys play an important function in filtering waste from the blood, and
putting them beneath pressure can lead to situations like acute kidney
injury or persistent kidney illness. Over time, kidney damage can impair the body’s ability to
take away waste and toxins, leading to long-term health problems.
Search recommendations from experienced users or trusted people throughout the fitness neighborhood.
Engage in conversations on respected on-line boards, participate in discussions, and ask for recommendations concerning dependable
sources. Nevertheless, at all times independently confirm the knowledge supplied to ensure its accuracy and relevance
to your specific needs.
If you endure from these results using compounds such as Cabergoline might help
to minimize back and stop them. Trenbolone acetate, generally known as ‘Tren A’ or ‘Tren Ace’ is known as the ‘King of steroids’ for a cause.
Experience Unparalleled Vitality and Endurance for Your Athletic and Skilled Pursuits.
Our scientifically-formulated products are designed
to optimize your bodily and cognitive capabilities, ensuring you stay ahead in each facet of life.
Shopping For Trenbolone requires careful consideration to ensure
compliance with legal rules and to keep away from counterfeit products.
When the blood vessels of the muscular wall
of the airways are constricted, Tren cough is triggered. We nonetheless don’t know precisely why this happens, but specialists
know it’s associated to a respiratory distress reaction.
The solely other avenue for buying Tren Ace besides black-market veterinary merchandise is to show to underground labs – a
supply you may be acquainted with if you’ve bought different anabolic steroids.
Trenbolone is a steroid that lets you build muscle and lose
fats simultaneously. This simultaneous effect
makes it a prime contest preparation compound, especially as
it’s a steroid that doesn’t aromatize, so you won’t be coping with fluid retention. Tren is
a steroid promoting hardness and a shredded
physique that’s dry, lean, and vascular. So, we will anticipate the unwanted effects to be significantly magnified in comparison with what you’d expertise even at excessive doses of testosterone.
This is crucial not only for well being causes but additionally to take care of the features you’ve made in the course of the cycle.
Low testosterone will outcome within the loss of muscle and the gaining of fat, basically destroying the hard work you set in during the cycle.
While it may be used for low season bulking, maybe
its most precious use is for contest prep and recomp
cycles, where you can use Tren Ace for shorter lengths of time at higher
doses. Your muscle features might be dry with Trenbolone,
so all the burden gained will be high quality and maintainable post-cycle.
Trenbolone Acetate has a relatively brief half-life, which necessitates frequent administration to take care of secure blood ranges.
However don’t be surprised whenever you find guys speaking about taking 500 or 850mg
– firstly, they could be very loose with the reality.
Secondly, if extreme doses are taken, it’s normally for a minimal amount of time earlier than the side effects turn out to
be unbearable. A larger dose during a cutting cycle of 200mg-300mg per
week can introduce extra problematic unwanted effects, particularly on the psychological side and issues like evening
sweats and insomnia.
As A Outcome Of trenbolone is a strongly androgenic steroid,
the DHT focus during the cycle will increase considerably and the variety of hair loss will increase.
Nonetheless, it is worth remembering that steroids often solely speed up
hair loss, so if you are not predisposed to baldness, this problem will in all probability not affect you.
I typically get questions like how many muscular tissues I can get by utilizing trenbolone.
The Trenbolone hormone itself was first created within the late 1960’s and the Acetate model would be offered beneath the names Finajet and Finaject.
The identical hormone would appear on the pharmaceutical market underneath
the name Parabolan and was manufactured by Negma Laboratories out of France.
This model of Trenbolone was comprised of the identical energetic hormone that
makes up Finajet and Finaject with the ester hooked up being the
one exception. It would even be the one Tren hormone ever manufactured for human use and could be discontinued in 1997 despite lots of therapeutic success.
Oxymetholone is an artificial male hormone (androgen/anabolic steroid) used
to treat a low purple blood cell depend. It
works by increasing the quantity of the hormone (erythropoietin) concerned in the
manufacturing of red blood cells. It is possibly one of many safer anabolic
steroids for females as a result of very low virilization effects in short-term utilization. Gynecomastia
is also not much of a priority, so there should not
be any have to add an antiestrogen if trenbolone is the only steroid
administered. The high androgen level resulting from this steroid, within the absence, is
extra estrogen, can even accelerate the burning of physique fat.
The end result ought to be a much tighter physique, hopefully with out the need for excessive dieting.
Cypionex is an androgen and anabolic steroid medication used
mainly to treat low testosterone levels in men and
can be used in hormone remedy for transgender
males.
As with any potent steroid, responsible use and adherence to really helpful dosages are crucial to keep away
from potential unwanted effects and ensure a optimistic bodybuilding experience.
When Trenbolone is injected into the body,
bodybuilders typically expertise immediate effects because
of its potent anabolic properties. One of the first instant effects is a rise in blood
circulate to the injected muscle group. Trenbolone enhances purple blood cell manufacturing,
resulting in improved oxygen delivery to the muscles.
This increased blood circulate can create a temporary feeling of fullness or pump within the injected area, contributing to
a way of tightness and enhanced vascularity. Identifying the correct kind
and gauge for Trenbolone injections is vital to ensure a easy and efficient administration process for bodybuilders.
Generally, bodybuilders opt for intramuscular injections, as they provide higher
absorption and minimize the risk of tissue damage.
Anavar is also recognized as protected owing to the
truth that it has the bottom androgenic rating
of only 24. Whereas Anavar may not be a wonder drug, the effects of
Anavar could be worn out and the chemical processes that take place can simply be examined
and documented scientifically. Now, don’t thoughts the joke,
the publish isn’t meant to warn you about steroids.
The worth of testosterone alternative remedy can vary, depending on the kind of ester prescribed and if a
patient has insurance. On common, our sufferers pay $100 per month for testosterone cypionate.
Ladies feel it at about 10mg women are a lot more delicate
to male sex steroids because women’s steroid receptors have
never experienced male sex steroids before. If you are wanting to increase your power
and turn into stronger, then a one rep max calculator is the best device for you.
A one repetition max calculator helps you establish your true
max reps before even beginning your workout routine.
It will assist boost up your performance and
stop accidents while doing so! A one repetition max calculator is
also a good way to track your progress and see how a lot weight you’ve lifted additional time.
It’s a great way to remain motivated and hold observe of your general progress.
Combining Anavar with Testosterone Enanthate can lead to significant results,
taking body transformation to the next degree.
Whereas all of them are the identical testosterone steroid, they come from totally different esters.
Testosterone enanthate and cypionate are mostly used because of their worth in addition to
ease of injection. Like Anavar, Testosterone is another steroid that may
be taken by novices without fearing many unwanted unwanted effects.
It can be utilized by both women and men and doesn’t have
any negative or nasty side effects. To top all of it, it comes with a 100-day money-back guarantee so that you don’t have anything to lose.
Anavar has a brief half-life of 9.4–10.4 hours; thus, we regularly
see bodybuilders take 2 x 10 mg dosages per day—once in the morning and
the other within the night. This will keep peak
serum testosterone levels somewhat than experiencing fluctuations from rare dosing.
Diligent customers will stick to moderate dosages, leading to important fats loss and minimal side effects.
However, it is worth noting that high dosages of Anavar could not burn significantly extra fats than a moderate dosage.
Our experience signifies a threshold for diminishing returns, where
an increase in unwanted facet effects happens, however not in outcomes.
Thus, it’s not advised to take dosages over 20 mg/day for males
and 10 mg/day for ladies. This may not sound like much weight, however visually, this will make a dramatic difference
to a person’s appearance.
At a dose of 80mg, every single day for the primary 5-6 weeks of the steroidal cycle is common or used for the duration of the cycle (if
6-8 weeks) when slicing. You can even improve the dose of Anavar additional time
to compensate for the tolerance the physique will begin to construct if
want be. As we discussed on this Anadrol cycle, Anadrol is utilized by bodybuilders to help improve muscle
mass and power. It is also used to scale back restoration time and enhance athletic efficiency.
For new customers of Anavar, itis really
helpful to start out with a conservative cycle to evaluate individualtolerance and response.
Take A Look At additionally increases pink blood cell production, thereby
bettering oxygen supply to muscular tissues and enhancing endurance.
These are simply some of the advantages that make
Testosterone a cornerstone in anabolic steroid cycles. Anavar, or Oxandrolone, is an anabolic steroid often utilized by bodybuilders
and athletes to reinforce their performance and obtain desired results.
Identified for its delicate androgenic properties, Anavar is famend for promoting muscle development, strength gains,
and fats loss with minimal unwanted facet effects.
As a well-liked option in numerous bodybuilding cycles, it’s valuable to look at the
outcomes and impacts of incorporating Anavar into one’s regimen. This would depend in your present food regimen, your aims, and the anabolic
steroids taken.
Conservative doses are used for each of these steroids in a 6-week
cycle. Anavar doesn’t want to be taken beyond this level, as we have seen masculinization happen in women running
excessively long cycles. However, these doses are enough for
important muscle and energy positive aspects. This can be a quick cycle
in comparison to these conducted in research.
Unlike steroids, where there’s often an unlimited difference between female and male
beneficial dosages, Clenbuterol permits both to use very similar doses.
As A Result Of females are, on average, smaller in physique measurement and weight than men, the
dose have to be tailored accordingly. Otherwise, the response
to Clenbuterol is very much the identical with both sexes.
Clenbuterol needs to be utilized in a method
that maintains its maximum effects for the total length of your cycle.
This means you should regulate the dose as the weeks go on, beginning
at fairly a low dose at the beginning of your cycle.
Many folks start off utilizing an all oral cycle, this
by NO means makes it a good suggestion. Wait until
you’re prepared to make use of an injectable and then try it out.
For your first cycle 50mg for 6 weeks will give you good
results offered your training/diet would have you ever including muscle without it.
This can be first cycle, so I type of wish to really feel things out.I was planning on doing it for four weeks, however I truly have yet to discover out the dosage.
I truly have read to take anywhere from mg per day so
I am kind of confused. Tbol might cause slightly extra side effects than Anavar, such as ldl cholesterol, liver enzymes and further testosterone suppression. I decided to run the pharmaceutical grade Anavar
I had at 20mg per day along with 200mg of testosterone per week for 6 weeks to take
a rest from the Anadrol.
Though Anavar will almost actually trigger a
discount in endogenous testosterone levels when used, even in small
doses, it can still be used alone. This cycle (in spite of getting a small quantity of Winstrol) can produce important muscle and strength gains.
Whereas Anavar is processed by each the liver and the kidneys, Andriol doesn’t result in any hepatic strain (as proven by studies).
Testosterone is more probably to increase each
muscle mass and energy and it is basically a bulking steroid.
Dianabol and Anadrol are two of the most highly effective steroids for gaining mass.
If you want to mix Anavar with different issues, make certain to use secure and effective strategies.
Before taking Anavar, seek the guidance of with a physician if you have
a medical situation or take other medicines. To get one of the best results from Anavar, it’s essential to search out the right
dosage.
Ernst Peibst is an skilled in anabolic steroids and PEDs with over
3,000 hours of analysis. He Is been educating individuals for 7 years by way of his
articles, written after finding out science papers, expert books and consulting
top medical doctors within the subject. Anavar is
considered one of the “best steroids” for women’s weight loss, if you’re determined to burn fats,
build muscle, and keep your feminine beauty. Girls
can typically expect to burn roughly 2-2.5lbs of fat
per week, in combination with going to the health club and dieting.
They won’t be turning into the Hulk (nor would most women want to), however the
elevated definition is a certainty, and with muscle replacing fats weight, any physique weight placed
on shall be lean muscle. Men on a slicing
cycle with Anavar can anticipate an excellent fats loss,
and it will be fairly fast as a result of Anavar is a quick-acting steroid that you’ll only
use for eight weeks max. Using Anavar at low to moderate doses is about as protected as it can get for anabolic steroid use.
Alcohol increases cortisol, a catabolic hormone that can blunt a
few of Anavar’s fat-burning and anabolic effects. High doses of Anavar give me again pumps and
jaw pumps as if I am chewing tough meat like beef jerky.
I by no means do over forty mg on orals as a result of back pumps are annoying, and never more than four weeks.
I’ve been on 60 mg cut up over three occasions a day for four weeks, and I’m getting some decrease back ache, stomach ache, and a really dark yellowish urine.
In clenbuterol’s case, as a end result of it
does not have an effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular
axis (HPTA) however as an alternative the central nervous system, ladies usually take an analogous dose to males.
Firstly, an individual can gauge their sensitivity to clenbuterol by
starting on a low dose and growing it steadily.
You might wish to do that as an alternative of taking Anavar alone as
a end result of the unwanted effects are much less harsh when you’re taking it simultaneously testosterone.
An Anavar with TRT cycle could be a great way to construct muscle and cut
back fat. The value of testosterone substitute therapy can differ, depending on the type of ester prescribed and if a affected person has insurance coverage.
On common, our patients pay $100 per 30 days for testosterone cypionate.
If someone has taken testosterone earlier than but not Anadrol,
this cycle will additional increase muscular power and hypertrophy.
Trenbolone, like Deca Durabolin, presents reasonable progesterone exercise, having the potential to
cause gynecomastia. Thus, users could wish to avoid utilizing SERMs
to stop aggravating progesterone levels.
Such a dose will assist in reducing body-fat, preserving muscle whereas on a calorie restricted food
plan and protect it as well while under strenuous exercise such as training.
Additional, the physique will seem more durable, tighter and all-in-all carry and possess a more pleasing look.
Before any girl will increase whole Anavar dosages beyond the 10mg vary she should be comfy at this initial dose and creep up in 5mg marks earlier than making a full leap to 20mg per day.
HGH is sort of always utilized in a stack as a result
of that’s where it is most helpful.
These kids have been taking average doses of Anavar constantly for six months to
eight years. The average bodybuilder will run Anavar for
a maximum of eight weeks. In our experience, ladies can typically expertise superior results in muscle mass compared to men on Anavar, even with a modest
dose of 5–10 mg per day. Actual, pure-quality HGH can not be produced in underground labs as a outcome of huge prices and
complexity. However, many Chinese labs look like manufacturing high-quality HGH,
which is sold as generic. Shopping For from such labs is a
gamble; you’ll want to know the supply earlier than handing over money.
This helps improve the muscle-to-fat ratio whereas decreasing restoration instances
so your downtime between exercises is lowered.
(Personally, I’ll use the drug for at least 6–8 weeks.) Spreading out my dose all
through the day at the similar tempo each time (20 mg/20 mg/20
mg) yields the greatest outcomes for me. Use 50 mg of clomid daily in the course of the post-cycle remedy part, and you must get well rapidly.
As A End Result Of bodybuilding ranges of
Oxandrolone end in a somewhat excessive suppression of testosterone, it is always recommended that males stack Anavar with Testosterone when using this steroid.
This is due to the fact that bodybuilding-relevant doses of Oxandrolone induce a relatively substantial reduction of testosterone.
However, it is predicted that this period
of recovery could be fairly quick (a few of weeks) earlier than natural testosterone ranges return to normal.
If you do decide to take Anavar on an empty stomach, make certain to drink loads
of water to help forestall any potential abdomen upset.
If you’re considering taking Anavar, it’s essential to
know the most effective time to take it, whether to take it with meals, and whether or not to inject
or take it orally. While not everybody will
expertise these unwanted effects, it’s necessary to focus on them
and to talk to your physician when you have any considerations.
This is more likely to occur in people who already have hypertension or different cardiovascular issues.
When planning your Anavar cycle, it is very important contemplate your targets and
regulate your dosage and cycle length accordingly.
If you wish to bulk up, you might want a better dosage and longer cycle.
By improving nitrogen balance, Anavar helps to create an anabolic setting that helps muscle growth and prevents muscle
breakdown. This blog publish explores the usage of Anavar
and its advantages for individuals who wish to
be as physically match as attainable. We explore the science behind this efficiency booster and shed gentle on how it may enhance your athletic abilities, from increased endurance
to rapid muscle repair. So buckle in and prepare to set out on a voyage that can redefine your capacity for efficiency.
Generally, Oxandrolone (Anavar) is simply given over the course of
a interval of some weeks.
To enhance efficient performance whereas taking Anavar must be
added to the special sports nutrition. If you speak to female health buffs and ask why they take Var, they’ll tell you that it’s because it will increase bodily energy
and endurance with out inflicting them to bulk up an extreme amount of.
“I was about to give up and attempt to buy actual anavar on-line once I got here across Crazybulk and their Anvarol product. As Anvarol buyer critiques show, it doesn’t aromatize and all the load you get hold of will be lean muscle mass.
This before-and-after image is the outcomes of long-term HGH use (several years of injections). This feminine consumer administers HGH daily for weight loss and anti-aging benefits; however, the dosages utilized are unknown. These are the outcomes of a user who blasted HGH for 10 days, taking megadoses of 16 IU per day.
As you presumably can guess, the Anavar’s results are far more highly effective and pronounced on a feminine physique compared to a person – that’s why the dosages of Oxanabol – Anavar for a lady should be means lower both. Remember, your dose might change based mostly on your weight and how a lot experience you have. Clenbuterol is often generally recognized as a lone wolf in the field of bodybuilding supplements due to its potent effects. However, there’s a vigorous debate going on about whether it can be efficiently used at the facet of steroids.
Whereas Clenbuterol has been proven in some animal studies to have an anabolic impact, there is no proof of this being the case within the human body. Clenbuterol is useful for people who use anabolic steroids as nicely as those who don’t. Some possible further severe issues are female-specific, although. Girls using Clenbuterol run the risk of fertility problems and disrupting the menstrual cycle.
It has been a widely used, respected, and very popular steroid for a very lengthy time and is certainly one of the few that females also can use because of its delicate androgenic results. Here, we are going to discuss every little thing you need to find out about this well-liked anabolic steroid, including its advantages, unwanted aspect effects, and tips on how to use it safely. We may also cover the most recent research and news associated to Winstrol, so stay tuned for informative and interesting content. Relying on Anavar’s strength enhance coupled with Winstrol’s muscle definition and fat discount capacities may present an interesting mixture.
However, should you use it for chopping, and full the cycle as described above, you will witness some incredible Anavar before and after differences. With Anavar, you’re not going to achieve large bulk—if that’s your thing you should be wanting at the more potent (and dangerous) Deca-Durabolin or Anadrol. In this article, I have put together everything you have to know about this steroid. It consists of the background on this synthetic, the results it provides and any unfavorable side effects that might be encountered. Some additionally point out the beginning of muscle definition, especially of their shoulders, arms, and back.
You know that understanding how a lot to take is just as important as knowing what you’re taking. If you’re looking for recommendations of how a lot should you take or elements to consider for the dosage, you’ve come to the proper place. The detectability of this substance within the physique can vary from three weeks to 4 months, depending on the testing mode. A urine check, for instance, can identify its presence for about three weeks post-use, whereas a hair follicle check might detect it for as much as four months. Components such as metabolism, dosage, and frequency of use can even affect detectability.
These unwanted effects of Anavar in women usually tend to be related to the female hormone and reproductive system. High-intensity interval coaching (HIIT) can be done regularly to help lower blood stress whereas also aiding in fat burning. Females, on the other hand, should monitor their cholesterol levels to ensure that their blood strain does not rise dangerously.
It achieves this by boosting nitrogen retention within the muscle tissue, thereby allowing them to contract extra while lifting. As a outcome, smaller muscle fibers that don’t usually get activated during workouts obtain enough stimulation, resulting in elevated power with out extreme bulk. Physique measurements, energy degree, energy, and mood can act as indicators of how the physique adjusts to the Winstrol solo cycle. However, if any uncomfortable or unwanted adverse outcomes begin to floor, it could be time to reconsider the continuing cycle. In conclusion, increasing Winstrol’s dosage may be an effective technique for superior users aiming for larger results, however it must be approached responsibly. Via cautious remark of non-public reactions and a readiness to make changes as essential, girls can successfully make the most of Winstrol at advanced stages of their fitness journeys.
Most cycles will prolong testosterone use past the eight weeks of the Anavar cycle, for a complete of 12 weeks, before beginning post-cycle remedy. Intermediate male Anavar users can improve their day by day dose to between 50 and eighty mg and still expect distinctive results supplied they maintain a rigorous food plan and coaching regimen. As we’re about to see, females may use and tolerate Anavar pretty properly, and even in very small doses, it might possibly produce wonderful results. Although it is simple logic that males require a higher Anavar dosage, you shouldn’t enhance your Anavar consumption to unreasonably high ranges.
To conclude, a 1-month Anavar bodybuilding cycle can provide feminine bodybuilders with a extra compact window to witness progress in strength, endurance, and muscle growth. Whereas these transformations may not be as intensive as these noticed in longer cycles, it’s still potential to realize measurable constructive outcomes. As with all Anavar cycles, responsible usage, a consistent train routine, and proper diet are critical to derive the maximum benefits and minimize potential dangers. The modifications would possibly range between individuals, but the cumulative results are probably positive, enhancing each athletic performance and bodily aesthetics.
The largest drawbacks of Clenbuterol would have to be that the side effects are insufferable and that it’s an unlawful compound. When using any Anabolic Steroid, it would be sensible to be certain to are wholesome earlier than using the substance. When using any compound, however particularly when utilizing two together, you must ensure you’re in good well being earlier than using them. I’ll additionally examine and show you the side effects you might experience and supply tips about the way to use them safely and effectively. If so, you may have heard of the powerful combination of Clenbuterol and Anavar.
By following proper dosage and cycle suggestions, customers can expertise
the benefits of Anavar whereas minimizing dangers. Remember to seek the guidance
of a healthcare provider earlier than beginning any cycle and think about post-cycle remedy to take care of stability.
For this purpose, Anavar is kind of always used as a
chopping steroid, which is the aim it excels at. Another advantage of Anavar for women in bodybuilding is that it’s thought of a light steroid.
This means that it’s less more probably to cause unwanted side
effects in comparison with other anabolic steroids. This is essential for ladies, as
they’re extra delicate to the effects of anabolic steroids than men. This can help to attenuate the danger of unwanted
side effects, corresponding to acne, hair loss, and adjustments of their menstrual cycle.
Not everyone will be capable of use Clenbuterol as a end
result of, at its core, it is a stimulant, and a few of us are too sensitive to the effects of stimulants to search out them of any benefit.
Even when utilized in a medical surroundings with skilled supervision, we nonetheless observe toxicity and
opposed results. Docs have efficiently prescribed Anadrol (oxymetholone)
for cachexia for a protracted time frame.
From this basis, they developed a product that achieves the same
results—but not from synthetic or modified compounds.
Regardless Of its low muscle-building potential in guys,
the anabolic nature of Anavar has a stronger effect on women. This means that women utilizing
this steroid will witness spectacular muscle features in only a few short weeks.
Simply like with any muscle-building process, correct food
plan and diet are very important for reaching desired Anavar outcomes.
Consuming a protein-rich food regimen will provide your physique with the mandatory building blocks for muscle progress.
Nevertheless, it’s essential to strategy its utilization with caution,
stick to applicable dosages, and contemplate the potential side effects to make sure
the advantages outweigh the dangers. Anavar, also referred to as Oxandrolone, is a steroid that
can be utilized in each bulking and slicing cycles in bodybuilding.
This steroid has grown in reputation lately as more and more girls use it to increase muscle
mass without gaining much fats.
Nevertheless, it’s necessary to do not overlook that these advantages don’t come without potential dangers.
Responsible usage, keeping monitor of unwanted effects, and recognizing the
necessity of ongoing monitoring—all these elements have to be factored in proper
at the outset. Winstrol, or as it’s scientifically known, Stanozolol,
is a widely used performance-enhancing drug.
It could be finest to live the healthiest way of life you’ll find a
way to whereas additionally eating loads of protein and calories if your objective is to realize muscle.
Ladies usually take Anavar for 4-6 weeks to
attenuate the danger of side effects. The unwanted effects of Anavar
for women embody potential masculinization, similar to deepening of the
voice and elevated body hair. For women who want a safer various, Anvarol is on the market and has been proven to give the same benefits as these acclaimed by Anavar,
minus the dangers. Figuring Out your physique completely and taking the proper dosages
will matter in your effort to deliver concerning the results you are really after for bodybuilding.
This combination is designed to extend girls’s muscle definition and improve total body composition. Women have been recognized to use Anavar to both
achieve muscle, lose fats, and even simply gain pure energy.
These drugs can improve pure testosterone ranges significantly (6, 7,
8). If a consumer is shut down severely, it is strongly recommended
to take all three of those medications simultaneously.
If someone has just taken Anadrol in average doses, they might solely take one
or two of those medication. There is evidence to recommend the
opposite is true when taking Anadrol with grapefruit juice,
which we’ve seen improve its bioavailability because of the fruit inhibiting CYP3A4 (5).
This is a liver enzyme that significantly reduces the absorption of many drugs (including anabolic steroids).
Conservative dosages have been used in this pattern cycle, with the risk of liver strain (and different
side effects) in mind. Our sufferers find regular cardiovascular exercise
helps to minimize large will increase in blood stress.
As mentioned, Anavar isn’t a critical bulking steroid—which has led to many guys considering it as a weak and ineffective drug.
Yet, whereas not ideal for enormous mass—with its muscle retaining and fats shedding results it makes it an ideal chopping steroid.
With these security considerations in thoughts, it may be price exploring various choices to attain muscle definition and
strength gains.
As a end result, it might possibly contribute to vital adjustments such
as increased lean muscle mass, reduced physique fat,
and improved muscle definition. One of the important thing advantages of Anavar for
women is its capacity to increase muscle mass whereas lowering
body fats. This ends in a more defined and sculpted look,
which is highly desirable for a lot of ladies trying to enhance their physique.
Men, specifically, can expertise lowered testosterone production with extended Anavar use.
This can lead to quite a lot of signs, including fatigue, mood changes, and decreased sexual desire.
Whereas Anavar presents numerous potential advantages for female bodybuilders and
athletes, it’s essential to acknowledge potential
side effects. Despite being thought-about a
mild steroid compared to others, caution is warranted.
Stacking Anavar and Winstrol can maximize each steroid’s benefits whereas minimizing unfavorable effects.
Anavar may help athletes enhance endurance and minimize fatigue,
allowing them to train more durable and for longer durations.
Anavar when taken in a reasonable dosage, doesn’t trigger
virilization. Most of such shady manufacturers combine Anavar
with Dianabol (which is one other oral anabolic) which is means cheaper.
Thus, necessary to buy Anavar from a trusted source or
you would end up buying a bunked product that may result in lots of nasty side effects.
Anavar is prone to be a safer steroid within the sense that it has fewer unwanted aspect effects.
Thus it’s fairly common for people to get scammed when attempting to buy anavar.
As a result, the risk is even greater when attempting to obtain this steroid as dealers usually cut the dose without you
understanding, or promote you fillers to extend their profit margins.
In bodybuilding circles, many believe Anavar to
be the safest steroid ever created. Doctors do prescribe Anavar
to youngsters with cachexia, demonstrating its low toxicity
however this doesn’t imply that it’s illegal and unsupervised use is safe as nicely.
#2 Experience – if you’ve by no means
been to the fitness center and are very inexperienced then it’s not essential to jump to performance enhancing
medication.
Expectedly, most of the anabolic steroids in every household have similar
attributes to at least one one other. In basic, probably the most generally used anabolic steroids fall into certainly one of three different families/categories.
Lastly, there are several options to those steroids which might be higher
suited to your needs. In addition, Winstrol is well-known for its
capability to extend strength and stamina.
This is partly as a end result of its capability to increase
the production of purple blood cells, which improves oxygenation of muscles and enhances endurance
throughout your workout, and during restoration. Anavar,
or Oxandrolone, presents a priceless device in the arsenal of fitness lovers and athletes aiming to realize their peak efficiency.
With its remarkable advantages in lean muscle preservation, restoration,
and metabolic enhancement, it stands as a flexible choice
for both cutting and strength-building phases.
This implies that Anavar might need much less impression on hair loss
than Tbol. Nonetheless, it’s clever to do not forget that Anavar can still contribute to hair loss, relying in your predispositions.
It’s important to notice that proper post-cycle therapy (PCT) and liver safety supplements are important when utilizing both Anavar or Tbol.
And as all the time, seek the guidance of with a
healthcare skilled earlier than considering the usage of
any anabolic steroid. Keep In Mind, whereas Tbol may be simpler on the
physique than another steroids, it’s nonetheless important to
method its use fastidiously and consult with a healthcare skilled earlier than starting any steroid
cycle. Although Tbol is usually considered to be safer than different
steroids, it’s essential to focus on the potential side effects and dangers.
As someone who has a keen curiosity in steroidal dietary supplements, I’d wish to share my insights on Anavar.
Our findings present that Winstrol extra severely impacts the
center compared to Anavar. Analysis supports this, revealing
that as little as 6 mg/day of Winstrol for six weeks can result in a 33%
reduction in HDL cholesterol—comparable to what’s noticed with 20 mg/day of Anavar.
Users of Winstrol often report issues with substantial intracellular water
discount, which can trigger muscle tissue to look deflated.
The capacity of this steroid to optimize nitrogen stability contributes to its effectiveness
as a muscle-building agent. In conclusion, the choice between Anavar and Winstrol hinges
on individual objectives, tolerance to unwanted side effects, and risk elements.
Consulting with a healthcare skilled or qualified fitness advisor is paramount
to devising a tailored method that aligns with one’s objectives and mitigates potential risks.
Anavar is understood for selling lean muscle mass, while Tbol is
best for growing overall muscle size.
With that stated, many athletes select Winstrol as a outcome of they are saying
it is better for muscle hardening. Anavar can cause
pumps with cardio, but Winstrol has a extra significant negative influence on joint health, ldl cholesterol,
and hairline. You should think about shopping for post-cycle therapy merchandise
for either a Winstrol or Anavar cycle. We beneficial you take a look at Rebirth
PCT reviews, or purchase Clomid or Nolvadex from our retailer for PCT.
This is typical of DHT-derivative steroids, with it being a potent male hormone.
Anavar’s capability to extend strength is believed to be related to the uptake of
ATP and fluid contained in the muscle cells. Girls are prone to build extra muscle
than men when taking Anavar, as a outcome of females having lower testosterone levels.
Progesterone acts similarly to estrogen and thus can stimulate
the mammary glands. Nonetheless, we find that trenbolone’s estrogen-like side effects are
extra noticeable when stacked with steroids that aromatize.
Testosterone ranges will almost certainly be shut down post-cycle, needing a powerful PCT to get endogenous testosterone back to normal levels.
We have seen bodybuilders successfully cycle the 2 together
just before a competition, trying lean, dry, and full.
Inside Bodybuilding does not condone the utilization of AAS via illegal means or for cosmetic use.
In this text, I will examine Anavar and Masteron based on their effects, unwanted
effects, and cost, to assist you make an informed choice about which steroid is
best for you. Ultimately, the choice comes right down to your individual targets and preferences.
As someone who has used both Anavar and Masteron up to now, I can offer some insight into the professionals and cons of every.
While each steroids have their benefits, there are some
key variations to assume about when deciding which
one to use. CrazyBulk is a reputable and well-known firm in the
fitness industry, and their products are formulated
with high-quality ingredients to make sure efficient and safe results.
Furthermore, it safeguards muscular tissues from damage and expedites their restoration,
allowing you to push more durable during training and
attain exceptional results.
Additionally, ATP manufacturing is increased with Anvarol supplementation, which results in explosive workouts.
So if you’re in search of a protected and authorized various to Anavar, then remember
to take a look at Anvarol. Finally, endurance and stamina are essential for bodybuilders because they permit you to train for longer durations of time and recover more shortly from your workouts.
Not an excellent record, however fortunately – it’s
really exhausting to get a sort of. You need to be vulnerable to
the effect and take excessive doses of the compound.
You won’t achieve a lot with it – each in bulking and slicing – but no different compound will give you THIS stage of element.
Due to this, CrazyBulk created Anvarol and Winsol – Plus other legal steroids.
So in conclusion, Winstrol offers you more energy to carry out better in your exercises and
Anavar gives you extra energy to burn fat.
70918248
70918248
This comprehensive guide breaks down every thing you want
to learn about Anavar for Sale, from identifying respectable products
to understanding proper use and avoiding common scams.
Pharmaqo is a leading steroid brand, offering high quality products to gym enthusiasts
for years. Before you order Anavar, it’s essential to grasp the
legal standing of the steroid in your country. In many places, together with the Usa, Anavar is assessed as
a managed substance, which means it is unlawful to
purchase without a prescription. In some nations, Anavar may
be out there legally over the counter or with a prescription; in others, it might be
totally banned.
You can achieve up to 7 Ib or three kg when you run a 20 mg/day standalone Anavar cycle
mixed with regular exercise and a caloric diet.
You may even lose as a lot as four Ib or about 2 kg of body
fat in the course of. Stacking Anavar with other steroid compounds like Testosterone Enanthate will give you even better bulking outcomes.
As an anabolic steroid – Anavar also comes with some side
effects that could probably be potentially harmful if not used properly.
This may cause the blood stress to rise to dangerous levels, putting the user in danger for a coronary heart assault or stroke.
As a result, these with hypertension ought to be very careful when contemplating
using Anavar. Excessive blood stress is one of the commonest medical conditions on the
earth, and it may possibly lead to a wide selection of
serious well being problems. When blood pressure is simply too excessive, it places further pressure on the center
and blood vessels, which might ultimately result in coronary heart
assaults, strokes, and kidney harm.
As a result, people who take Anavar may be at an elevated risk of developing heart illness.
In addition, Anavar may help to extend bone
density and enhance blood circulation. As a result, it’s an effective tool for serving to to construct muscle and improve athletic efficiency.
Consultation with professionals who’ve experience in performance-enhancing substances can present invaluable guidance tailored to your particular
wants. By taking these steps, you can harness the potential benefits of Anavar while minimizing the risks, paving the finest way for a
profitable fitness journey. The security or
effectiveness of the steroid can be affected by factors
like age and gender.
Remember, slicing corners to economize on anabolic steroids can result in dangerous consequences.
Instead, spend money on genuine merchandise from respected suppliers to attain your
fitness goals safely and successfully. Anavar is well known as the one anabolic steroid ladies can use with little to no risk of side effects
– so lengthy as doses don’t exceed 20mg per day.
Nonetheless, another compounds are also utilized by females, including Winstrol and Primobolan, as
well as the fat-burning compound Clenbuterol.
You ought to make certain that you are utilizing efficient contraception when taking this
medicine and let your physician know instantly should you turn into pregnant
whereas on this medication. Throughout your oxandrolone treatment, you
will want to get common blood and urine checks. This is to
ensure that you might be not affected by any serious unwanted side effects brought on by the
oxandrolone. This will forestall any issues from becoming very severe since they
are going to be caught early. Anavar might or will not be safe depending upon your discipline to follow its doses and cycle.
The gastrointestinal lot retains the medicine, which arrives at its best
serum focus in no less than an hour of admission.
Anavar can enhance the degrees of LDL cholesterol
(the “bad” cholesterol) in your blood. If you experience any modifications
in your pores and skin shade while taking Anavar, you need
to report them to your doctor. In most circumstances, the discoloration will resolve by itself when you stop taking
the treatment.
Together With loads of healthy fats in the food regimen will add to
danger reduction. Adverse modifications to cholesterol
levels, as can be attributable to Anavar, can heighten your threat of heart-related disease and
even stroke. In some individuals, LDL levels may be increased (this is the “bad” kind of cholesterol), whereas the “good” ldl
cholesterol of HDL is decreased. While you’re utilizing the steroid, you
won’t have symptoms of low testosterone. Still, as quickly as you cease taking Anavar,
and the place no other type of exterior testosterone is being
taken, you presumably can expertise a sudden drop in T
ranges – particularly as Anavar leaves the physique shortly.
Optionally, you can use DHT-blocking prescription medications to assist stop hair
loss during Anavar use, though these can include their unwanted effects,
similar to lack of muscle, so communicate to
your physician. But being based on a really highly effective androgen in DHT,
Anavar can include the danger of androgenic side effects if you’re somebody who’s already
genetically predisposed to them.
Clients appreciate their thorough approach, as Elite Performance Gear offers detailed product data, including ingredient
lists and verified lab outcomes. If the steroid is stopped
quickly enough, these results should reverse and go away.
However if Anavar continues to be used, it can be harder to reverse or deal with virilization effects the more they’re allowed to develop.
UGL sources can value roughly than this – costs vary considerably across suppliers,
and so does the standard.
Anavar can produce some gentle androgenic results in men, and hair loss can be certainly
one of these issues for males who’ve a genetic predisposition to baldness.
Anavar isn’t essentially the most suppressive steroid, but your pure testosterone manufacturing is
likely to have taken a hit. This may cause symptoms of low testosterone
when your cycle ends, together with loss of muscle and fat acquire.
In all but essentially the most extreme circumstances, girls wanting to realize most leanness will focus on attending to
10%-15% physique fats.
This is basically produced in a non-certified laboratory and poses a high risk to the consumer, as there are no laws in place to ensure product safety.
If you’re getting high quality oxandrolone, you’ll love
the strong, dry gains. The main function of post-cycle remedy is to restart endogenous testosterone
manufacturing. This aids in normalizing hormone ranges for optimal physiological and psychological health, as properly as retaining results from a cycle.
In Thailand, the regulation states that Anavar shouldn’t be issued out through a prescription because of
anabolic steroids being Class S controlled medication. Nonetheless, bodybuilders visiting Thailand have reported shopping for Anavar
from local pharmacies with ease. This is commonly possible and not utilizing a prescription, though a Thai doctor can also problem a prescription in change for a small charge.
One of essentially the most significant cons of Anavar is
its potential to trigger liver toxicity. This is because the
drug is metabolized by the liver, and over time, this will result in injury to liver cells.
It can happen in each men and women, and it’s most likely to happen if you
first begin taking the drug. As a result, Anavar may help to improve the strength and density of bones, making them much less more probably to
break. This may be extraordinarily useful for athletes
and older adults who’re in danger for fractures.
Combining Winstrol (Stanozolol) and Anavar (Oxandrolone) in a cycle
has turn into a go-to choice for bodybuilders and athletes
aiming to achieve a lean, toned physique. Winstrol
and Anavar are famend for his or her chopping properties, serving to users achieve muscle definition with
out including significant bulk. Nonetheless, the pre use levels won’t return again overnight, is requiring a minimum of a quantity of months, but generally it could be
even as much as a full yr. This is the principle purpose why most males are going to want to introduce a Submit Cycle
Remedy (PCT) plan to have the ability to assist with the restoration. In truth,
this follow is recommended to anyone who used
steroids because it greatly helps. Anavar (oxandrolone) is an anabolic
steroid that is typically utilized by both men and women for efficiency enhancement
and muscle-building functions.
When you purchase Anavar on-line, you achieve entry to a flexible anabolic steroid famend for its effectiveness and minimal unwanted facet effects.
With the comfort of purchasing Anavar in Australia, you
can confidently integrate this powerful compound into your health journey.
Improve endurance, burn fat, and expertise improved muscle
hardness with Anavar’s advantages. Whether Or Not you’re
a novice or seasoned athlete, Anavar is often a valuable addition to your
routine.
This permits us to realize perception into how completely
different folks expertise Anavar. So, we all know that Anavar is insanely efficient at delivering excellent outcomes, but on the end of the day, steroids aren’t for everybody.
Sure, all of us need the results, however plenty of guys nonetheless won’t make
the leap into actually utilizing a steroid like Anavar.
This assumes you aren’t utilizing excessive doses of Anavar and never utilizing it continually
over a protracted period.
Cycles should be limited to six weeks, and the dosage should be
10mg daily. Some women would possibly wish to go further
and add another two weeks to the cycle while increasing the dosage
for these last two weeks up to 20mg every day, but monitor for any potential unwanted side effects.
Testosterone must be included in a complicated
Anavar (Oxandrolone) cycle, even when at only a maintenance dosage of 100mg weekly along with your chosen ester, with propionate or enanthate being frequent selections.
The liver enzyme values are going to be elevated whereas
administering with this steroid. Elevated liver enzymes doesn’t imply that the liver is damaged, however which means it might be broken in case correct measures won’t be taken. Although it is hepatotoxic, it is
important to observe that Oxandrolone is considered one of
the milder steroids as there are others out there that are thought of to
be a lot much more worse.
On a quantitative scale, Anavar boosts muscle mass progress by 44%.
Taking into consideration that its distinguishing power is basically fat decrease, the place bulk takes a secondary lounge, a 44% protein synthesis increase
is incredible. Sure, Anavar 50mg is usually used by women due
to its comparatively delicate androgenic properties.
However, the dosage must be fastidiously managed to avoid virilization results.
Pharmaceutical-grade Anavar was synthesized by scientists in a licensed laboratory when it was legal for medical reasons.
Stringent regulations were in place for maximum security
and success. This was prescribed to sufferers suffering from cachexia, where muscle loss was occurring at an alarming fee, growing the chance of mortality.
50mg every day is the best standard dose to steadiness fascinating benefits and side effects.
Few Anavar users will find a have to take the dosage past 50mg, and
most men admit that they don’t see the benefits they anticipated beneath 50mg.
But that’s only one facet of the story… Efficiency doses take
issues to a model new degree because we wish
to profit from Anavar’s anabolic effects beyond what’s required in medical therapies.
This is one cause why men, in particular, will choose not to use Anavar – the excessive price combined with the status
it has of being “too mild” can definitely put you off. Still, we must
always remember that even a 4-week cycle of Anavar can produce outcomes, which is in a position to hold
costs down somewhat. Notice that this doesn’t
essentially imply it’s authorized to import or promote AAS in such nations – legal guidelines
differ.
This is basically produced in a non-certified laboratory and poses a high threat to the patron, as
there are not any rules in place to ensure product security.
If you’re getting high quality oxandrolone, you’ll
love the strong, dry positive aspects. The major function of post-cycle
remedy is to restart endogenous testosterone production. This aids in normalizing hormone levels for optimal
physiological and psychological well being, as nicely as retaining outcomes from a cycle.
In Thailand, the legislation states that Anavar shouldn’t be
issued out via a prescription as a outcome of anabolic steroids being Class
S controlled drugs. However, bodybuilders visiting Thailand have reported buying Anavar from local pharmacies
with ease. This is usually possible without a prescription, although a Thai physician can even issue a prescription in trade for a small fee.
While it’s not as well-known as other anabolic steroids, Anavar has been confirmed to offer a number of
benefits that make it a top choice for athletes and bodybuilders.
Athletes and bodybuilders typically use Anavar to enhance muscle mass, strength, and efficiency.
It is known for its capacity to advertise lean muscle mass without
inflicting significant water retention or estrogen-related unwanted effects.
Implementing a post-cycle therapy (PCT) protocol after completing an Anavar (Oxandrolone) cycle is crucial for
restoring pure hormone production and maintaining optimum well being.
Anavar 50mg x 60 Tabs (Oxandrolone) it’s the strongest and
in style steroid to be used in the slicing cycle by men or bodybuilders.
It is properly tolerated and very efficient with no
bloating side effects. Oxandrolone helps to extend protein synthesis within the physique, which helps to extend muscle mass and energy.
The drug additionally improves nitrogen stability, which helps to speed up
recovery after exercises and stop muscle tissue breakdown. Anavar, acknowledged as
some of the well-liked oral anabolic steroids, boasts distinctive tolerance by the physique.
Its distinctive feature lies in its capacity for use by both men and women with minimal unwanted side effects, setting it aside from
different compounds. However, the true potential of
Oxandrolone is commonly overshadowed by unrealistic expectations, attributing to the moderate
exposure it supplies.
While it is rather well-tolerated signs of virilization can happen however they are uncommon and very rare if the woman plans her Anavar cycle
in a responsible method. Anavar is doubtless certainly
one of the in style slicing steroids (anabolic steroid) designed for weight
loss solutions. It is particularly used by men and women because of its immense popularity and fast fat-burning capability.
The outcomes of the medication will be enhanced when combined
with a nutritious diet. This is a testosterone derived
steroid; such as Sustanon or Testosterone Enanthate, which is used
for much longer than the “kick start” (8-10 weeks). This is
finished as a outcome of usually, the primary steroid
takes a quantity of weeks or months to totally become lively within the blood and give the person its primary positive
results. So a secondary steroid is used that “kicks in” far quicker
and is usually an oral, corresponding to Anavar.
For many women, value alone would be the determining factor when selecting
to use both HGH or Anavar. Although HGH is a hormone, it’s a very different
hormone from testosterone and other hormones we are acquainted with
when utilizing anabolic steroids. It has nothing to do with steroids,
and that’s something we have to be clear about from the start.
Masteron, being a more potent steroid, carries the next danger of
unwanted facet effects. Anavar is considered milder and fewer likely to trigger severe side
effects, making it a well-liked option among beginners and girls.
Possible side effects embrace liver injury, ldl cholesterol issues, and hormonal imbalances.
As Quickly As you begin stepping into the higher
finish of dosing, you’ll need to cut up it in two,
and sometimes three injections per week; in any other
case, the dose being injected directly becomes overwhelming.
Post-injection ache is often felt with Primobolan – another excuse
why injecting extra incessantly is most popular.
As you’ve in all probability guessed by now, I completely prefer injectable Primobolan and recommend it as the greatest way
to go for male users. Females taking very low doses of Primo are perhaps the one situation where it is smart to use orals.
Any ideas on how I can improve what I’m doing or if that’s
an excellent cycle?
If cycles are stored quick and dosages stay modest, any
hair thinning may be reversed post-cycle. Anavar Prohormone has carved its niche within the bodybuilding world as a potent ally in chopping
cycles, aiding athletes and bodybuilders in attaining lean, shredded physiques.
Its scientific backing and the plethora of success stories
from real-world users make it a compelling option for these
trying to improve their chopping cycles and obtain their body composition objectives.
Anavar is a potent anabolic steroid that may help in muscle development and fats loss.
Although it isn’t as well-known as a variety of the different supplements
out there, many bodybuilders utilize it to succeed in their fitness objectives.
Anavar will offset any water retention attributable to testosterone and
will dry and harden your physique. Anavar is a
comparatively mild steroid and very tolerable when it
comes to unwanted effects. This cycle focuses on fat loss, whereas Testosterone Propionate will keep lean muscle
and that critical energy you need whereas on a calorie deficit food plan. Results from a Take A Look At
Prop cycle will be formed by what you’re aiming for – this steroid
will help you retain muscle if you’re dieting for contest prep or different cutting
goals. Testosterone Propionate is a steroid that even first-time customers can typically comfortably use at doses
that more advanced customers will take. There is hardly a greater
introduction to using AAS than this, and unwanted effects
shall be minimal or non-existent. As I near the tip of my cycle, I begin to taper off
the dosages steadily.
Masteron’s advantages are a few of the most specific
you will find amongst any anabolic steroid. Masteron comes with
out water retention, so it supplies a powerful addition to a slicing cycle where fats loss
is desired and an total physique enhancement that suits the most severe customers.
Being based on DHT, which is significantly more androgenic than testosterone itself, Masteron poses relatively excessive risks of
virilization for female users. As a rule of thumb, most females
are suggested to not exceed a every day dosage of 15 milligrams.
It won’t do much to instantly promote fat loss apart from boosting the metabolism, which is
at all times welcome. What it does very properly is assist the
body shed water, and this naturally results
in a physique that appears lighter and extra outlined.
Winstrol’s anabolic effects will play some role in helping you get rid of fat – however provided that you’re on a calorie-deficit
diet and doing intensive common cardio work. Just like Winstrol,
Primobolan won’t give men much of a muscle achieve boost, but it’s going to present
some vital lean positive aspects for females and a discount in body fat.
Primobolan is perfect for cutting as it could possibly immediately promote fats loss, which Winstrol doesn’t do.
Both Anavar and Winstrol may be poisonous to the liver, but Anavar
is generally thought of to be less toxic. Anavar is a 17-alpha-alkylated
steroid, which means it has been modified to move through the liver without being broken down. This can put extra stress
on the liver, but Anavar is less poisonous than different 17-alpha-alkylated steroids.
It is necessary to notice that Anavar is a managed substance and should only be used beneath
the supervision of a healthcare professional. If you expertise any of these side effects, you should cease using Anavar
instantly and seek medical attention. Different esters have different detection occasions based on their half-life and how long they take
to clear the physique to a low sufficient degree to keep away from detection. This can be anywhere from a
couple of weeks to 3 months after your last injection.
Though Primobolan contributes little to muscle acquire, Winstrol does present
some scope for mass acquire during this cycle.
No one makes use of Primo on the lookout for important muscle positive aspects; there are lots of other higher AAS for that.
However, reasonable gains are potential, and some guys will see a
friendly 10 lbs of quality lean muscle in a typical Primobolan cycle where
it’s the primary anabolic compound. Whatever gains are made with Primo, males all
the time discover they are QUALITY positive aspects.
Primobolan is doubtless considered one of the few
steroids we can successfully use for either bulking
or slicing. Although it’s not in the identical league as our favorite bulking steroids
as a outcome of Primobolan is a comparatively weak and
gradual muscle builder, you get high quality gains. Still,
these are slower features, and longer lean bulking cycles are the place Primo excels.
One of the primary attributes that units winstrol other
than different steroids is that it doesn’t convert into estrogen, which has many advantages.
Most folks experience some extent of water retention with most steroid medications, together with Anavar and Winstrol.
When it comes to choosing between Anvarol and Anavar, Anvarol is
the safer option. Anvarol is a natural complement that’s designed to promote lean muscle
growth, which makes it a extra health-friendly possibility when in comparison with Anavar.
A double-blind examine states that weightlifters
given 14 grams of BCAA day by day lost 1% more fats inside eight weeks.
Wild yam root extract helps regulate excessive metabolism, supporting fats loss
efforts.
And while its muscle gains might be more modest when in comparison with the bulking you get when Anavar, they will be
extra practical and sustainable after you stop. Below, you’ll learn extra about how to
dose Anavar properly and the greatest way to cycle it through your
system. In this way, you’ll have the ability to take it and decrease your potential unwanted effects safely.
As a result, most men sometimes don’t endure from elevated
levels of this hormone.
Calorie consumption ought to be tailored to a user’s objectives when cycling Anavar.
Therefore, if Anavar is taken with the intention of bulking and gaining lean mass, then a small calorie surplus could additionally be adopted to boost muscle and power outcomes.
We have discovered clenbuterol to trigger cardiovascular pressure in some
customers, potentially inflicting myocardial injury (33).
This is due to extreme stimulation of the CNS, causing elevated ranges of epinephrine.
Consequently, a user’s heart fee can velocity up and turn into enlarged (34).
Nevertheless, steroids work different on everyone, therefore
not everybody who makes use of steroid achieves the same consequence.
The false impression that Anadrol cycles are
unsuitable for girls may be attributed to bodybuilding’s lack of practical knowledge relating to steroids’ results on females.
This is as a end result of of steroids being much
less generally used among women, leading to much less retelling of personal expertise in the fitness group.
In truth, it remains one of the solely steroids in studies where girls
can take megadoses of it and nonetheless not expertise virilization.
Yes, all steroid cycles should be adopted up with post-cycle remedy to both
retain your gains and restore your regular hormone function. The PCT you undertake after using Anavar and
the timing of it’s going to also be decided by another steroids you’re utilizing.
A fundamental PCT cycle should consist of SERMs
similar to Nolvadex and Clomid, which may be much more environment
friendly when mixed with HCG. Wait 14 days submit cycle to begin recovery and use 50mg/day
Clomid for 20 days and 0.5mg/day Arimidex alongside it.
Masteron can also be an AAS typically described for a selected use, but
I’d call it slightly more versatile than Winstrol.
Winstrol is a unique steroid, but BOTH provides you with wonderful aesthetics
which might be match for aggressive purposes. One of the
most popular cycles is Masteron Enanthate, Testosterone Enanthate, and
the powerful anabolic compound Trenbolone Enanthate. Since they all
use the identical ester, these compounds are very appropriate with one another and produce excellent results for aggressive bodybuilders,
especially in a pre-contest cycle. Masteron is infamous for rising your libido, typically to a point the place it’s unwelcome.
Masteron, of course, retains much of its DHT father or mother mechanisms of motion.
In any case, you’ll most likely flip to the tried and examined PCT drugs in Nolvadex and Clomid, which both help stimulate testosterone production. This stack could have zero water retention, and Anavar will boost your fats
loss capabilities. Power and muscle preservation will be
excellent, even on a calorie deficit. Lean, onerous, and vascular with an unimaginable boost to motivation,
power, and confidence courtesy of Masteron. This easy but powerful lean bulking cycle may
have Masteron decreasing any water retention whereas
testosterone will stop a crash of your estradiol ranges.
For best outcomes, your diet must be somewhat above upkeep energy.
The type of results you’d anticipate from a chopping steroid like Anavar is increased
muscle hardness, density and vascularity. Anavar may help to increase strength and endurance,
which can be helpful for athletes. If you are figuring
out two times per week – we suggest starting with 50mg of Anavar per
day. For occasion, if you’re working out four times per week – we advocate
starting with 20mg of Anavar per day. If you’re working out greater than thrice per week, we suggest starting at the lower finish of the dosage range.
We have seen this cause vast quantities of water retention, especially when users’ diets contain sufficient amounts of sodium.
We find high dosages of any oral steroid trigger notable fluctuations in HDL and
LDL ldl cholesterol by way of the stimulation of hepatic lipase, an enzyme that
has a detrimental effect on ldl cholesterol.
We find that an Anadrol cycle adds significantly extra lean muscle
tissue than an Anavar cycle. Nonetheless,
Anadrol’s fat-burning results usually are not as pronounced as a outcome of Anavar’s positive results on insulin sensitivity and T3 (triiodothyronine).
We have also discovered Anavar to increase T3 (triiodothyronine) ranges (1), whereas enhancing
insulin sensitivity, leading to a discount in subcutaneous and visceral fat.
Thus, females can reap the benefits of a simultaneous muscle-building and fat-burning effect.
It’s additionally recommended to use on-cycle help dietary
supplements during an Anavar cycle.
Anavar is regarded as particularly efficient for restoration as a outcome of its comparatively low
toxicity to the liver and its lack of estrogenic effects.
While other steroids might supply related benefits for damage restoration, Anavar stands out due to its milder facet impact
profile. Oxandrolone (Anavar) is an androgen and artificial anabolic steroid (AAS)
used for a quantity of functions. Of explicit curiosity is its remedy of burn accidents, which overlaps in some ways with injuries via weightlifting.
You can also stack all three of those collectively for max fat loss and muscle
positive aspects. It’s also price noting that the one unwanted effects
reported by the ladies on one hundred fifty mg
per day were decreased libido and elevated fatigue, undoubtedly
the end result of lower endogenous testosterone production.
Anvarol is formulated to imitate the results of Anavar without the legal dangers.
It contains Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), a compound vital for
muscle growth and restore, which can contribute to
improved power and endurance throughout workouts. At the
one-month mark, customers can anticipate even higher transformations of their
physique. Whereas particular outcomes might vary, most people report noticeable enhancements in energy and
muscle definition.
Moreover, we now have discovered common cardiovascular coaching to have a notable
reductive effect on blood strain in our sufferers.
PCT after 7 days- Clomid/Nolvadex + HCG 250iu twice weekly
so that you remain fertile. When it comes to building
a large and ripped physique, the mix of Anavar and Testosterone provides you with a potent combination of compounds!
Anavar is considered an anabolic steroid by the World
Anti-Doping Affiliation and is, therefore, banned for competitive functions.
Winstrol and Primobolan are often stacked with Anavar to
bolster strength and lean muscle gains. We have observed this duo produce notable fats
loss and moderate increases in lean muscle mass,
starting from 10 to twenty kilos. One of the primary benefits
of Anavar is its ability to increase muscle mass and strength whereas
concurrently burning fats. This makes it a
preferred alternative for athletes seeking to enhance their performance without including extra
weight. Additionally, Anavar is understood for its low threat
of inflicting androgenic unwanted effects corresponding to zits and hair loss,
making it a safer choice for each women and men. It displays decrease androgenic properties, decreasing the danger of virilization unwanted effects.
This guide helps to run an efficient Anavar cycle
to maximise its outcomes. It is certainly one of the best
options for novice customers and the right selection to realize spectacular strength.
Anavar, a popular anabolic steroid, has garnered consideration for its potential to advertise muscle features, improve power, and help in fat
loss. While everyone’s physique responds in a special way,
two weeks is usually considered an important milestone to evaluate initial progress
and glimpse the transformation that Anavar can facilitate.
This dose will increase mass and energy while minimizing the risk of common androgenic results.
If it’s your first time using YK-11 and unwanted effects concern you, starting low at 5mg per day will nonetheless
get results.
Many believe Primobolan is better suited to girls than Winstrol
is and, normally, should have fewer side effects.
Primobolan additionally comes in oral and injectable varieties and, like
Winstrol, is a DHT-based steroid. This means no aromatizing and no estrogenic effects like water retention.
Winstrol is generally simple to find and legally bought in many other international locations,
together with India, Greece, Thailand, and Egypt.
Underground lab setups haven’t any hygiene or high quality control necessities, so your risks
are heightened. Besides safety and sterility issues, another big concern with underground labs is their tendency to underdose a steroid.
This could be done on objective to economize or unintentionally merely because of a
lack of knowledge or experience in manufacturing.
This means Stanozolol comes with no estrogen-related unwanted side effects in any respect.
When we measure Winstrol’s results, it’s not often in the amount of muscle gained or fat misplaced.
However, most Winny customers will depend on different AAS or SARMs
to bulk and lose fat (see my Winny/Clen stack later on this guide).
A common strategy on a Winstrol cycle is to use your snug most dosage within the final week or
two earlier than a competition and a lower dose earlier.
Winstrol is thought medically for its benefits to bone well being and bone strength.
Potentially, Winstrol may provide some strength improvements to
the tendons.
Customers of Anavar should have their blood creatinine levels monitored
typically before, throughout, and after cycles. There is
still an opportunity that your blood strain can increase considerably, however
you may be certain that it’ll return to regular after
the cycle is full. Therefore, customers should be ready for
some strain on their cardiovascular system, which is in a position to
moderately increase their risk of myocardial infarction. There is at all times a direct affiliation between enhanced strength,
size, and health club efficiency and elevated testosterone
levels. As part of the remedy for HIV/AIDS, the drugs was used
to encourage the development of new muscle tissue in patients with illnesses that trigger unintended
weight loss. In some cases of osteoporosis, it has
additionally been demonstrated to be considerably efficient as a therapy.
Stacking is the popular method of obtaining large outcomes with Sustanon 250, and as a sophisticated person, all different
steroids are on the desk. Nevertheless, females who select to use Sustanon shall be properly conscious
of these dangers and may usually discover the trade-off is value it
for the lean muscle and physique transformation that can be achieved.
Most men discover that their temper improves – their outlook on life becomes more constructive and motivated, and confidence will increase.
This is a pleasant bonus profit we don’t usually
consider until we’re on a cycle. There are actually some basic expectations that all Sustanon 250 customers will see results from a normal cycle.
Many SARMs have an disagreeable taste, so observe it
up with water or a nice-tasting drink to eliminate the style.
There are two exceptions to this liquid administration – if you’re
taking SR-9009 or SR-9011, you need to maintain the liquid underneath your tongue for a couple of minutes to absorb
it. If there’s still any formula left after that time,
you possibly can spit it out and rinse it with water.
Anabolic steroids bind to many androgen receptors all through the physique.
This is how we get such a significant discount in androgenic-type
side effects while still getting advantages like muscle growth.
Each SARM is completely different, but most are designed to bind to skeletal muscle tissue receptors.
This stack ought to be an 8-week cycle; ideally,
you’ll enhance your dose as you go.
Nolvadex is effective at 40mg every day for the first two weeks, then lowered to 20mg daily for the final two weeks.
Either of these (Clomid and Nolvadex) will usually be mixed with Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) to
set off the manufacturing of testosterone. HCG will
often be taken for eight weeks for PCT functions, somewhere between 500iu and 1000iu day by day.
One of the best things about testosterone steroid injections is
that they present no stress to the liver. So, Sustanon 250 just isn’t going to trigger modifications to your liver enzyme values.
Sustanon 250 will often be used in a stack, and this could include oral
steroids, that are toxic to the liver.
Thus, an Anavar and Winstrol cycle is commonly utilized by intermediate or superior steroid users, on the
expense of doubtless increased complications. Our lipid profiles
indicate that testosterone is cardiotoxic, though less so
than different anabolic steroids. Moreover, testosterone just isn’t significantly hepatotoxic, as it is an injectable steroid.
Hepatic and cardiac well being are the two primary considerations we’ve when someone is using anabolic steroids.
Female newbies, however, are suggested to start out with a lower dosage of roughly 5-10mg per day.
Ladies are extra sensitive to androgenic results, so it is essential, to start with a conservative dose to avoid unwanted unwanted effects.
Genetics would be the main think about how bad your hair shedding is, so if you’re lucky sufficient to maintain a full head of hair, you’re within the minority.
Even guys who aren’t normally vulnerable to
male sample baldness with other AAS can see some hairline receding and hair shedding.
The timing of PCT, the place Masteron is the first
AAS, will mean beginning post-cycle therapy
two days after your last injection.
A one repetition max calculator can additionally be a great way to trace your progress and see how much weight you have lifted extra time.
Bear In Mind, Anavar is a potent compound, and accountable utilization is
vital to attenuate potential risks and maximize its benefits.
Therefore, it is crucial to strategy purchasing it with diligence, research, and caution to make sure you are acquiring a protected and legit product.
The aesthetic results you can achieve with Masteron are dramatic and spectacular, making this a favorite steroid
within the bodybuilding and physique competitors.
We have had success in accelerating the restoration of women’s endogenous testosterone when supplementing with DHEA, the official prescription treatment for
ladies with low androgen ranges. Testo-Max is made with a mix of pure ingredients which
have been confirmed to spice up testosterone ranges.
If you will say ignorant issues in right here
perhaps you need to go elsewhere. In nearly 20 years I’ve
never seen real anavar trigger androgenic unwanted effects in a girl underneath 20mg a
day. In some cases, virilization may be irreversible even after
the person stops taking steroids. As a result, many female athletes choose to keep away from
Anavar altogether to reduce their risk of growing unwanted masculine traits.
For men, Anavar abuse can suppress testosterone manufacturing,
resulting in decreased libido, infertility, and various sexual
well being problems. These hormonal disruptions can even cause temper
swings and emotional instability. It’s necessary
you maintain a thorough listing of all drugs, together with over-the-counter medication and supplements.
Anavar must be sourced fastidiously to ensure you get what
you want – correctly dosed and high-purity Oxandrolone (preferably pharmaceutical-grade).
Availability and ease of entry, authorized situations, and pricing of Oxandrolone will differ throughout totally different elements of the world.
And similar to the constructive outcomes, the quality of your Anavar can play a
BIG half in the types and severity of unwanted effects.
This is another excuse we should keep away from poor-quality
Oxandrolone on the black market by solely shopping for from
dependable suppliers.
Experienced customers may have greater doses due to receptor
desensitization and physiological variations. It’s a common practice to take steroids, similar to Anavar, for performance enhancement.
With their powers to construct muscle and
cut back fat come some unwanted side effects that always raise alarm bells.
Such a mentality means not caring about water retention,
which leads to puffy and bloated muscle tissue. This extreme water/fluid retention is a half of the rationale why so many pro bodybuilders are being criticized for having ‘ugly’ physiques today.
Anavar works by rising protein synthesis and nitrogen retention within the muscle tissue,
which finally ends up in elevated muscle mass and power.
In conclusion, just like with any treatment, the potential for side effects exists with Anavar, but they usually
manifest when misused or abused. Therefore, adhering to really helpful guidelines, together with proper dosage and cycle
size, and prioritizing total well being via a balanced
lifestyle can considerably mitigate these dangers.
When considering Anavar, you would possibly surprise if it is really secure and what unwanted side effects may arise.
You Have likely heard about its advantages for certain medical conditions, but the dangers cannot
be ignored. Nausea, acne, and even liver toxicity are potential issues, to not mention hormonal
imbalances that might influence both men and women in another way.
It’s important to weigh these elements fastidiously, particularly should you’re excited about utilizing it
without medical supervision. What security measures might mitigate these
risks, and are there hidden dangers you haven’t but considered?
Guaranteeing the prioritization of your health and security is absolutely vital,
as it types the foundation for a satisfying and well-balanced life.
Keep In Mind, responsible and knowledgeable usage of steroids is important to mitigate potential
risks and maximize the advantages, ensuring
that you’re on the right path towards reaching your desired results.
NPP stands for Nandrolone Phenylpropionate, which is a popular anabolic steroid.
It is a modified type of nandrolone, which is a naturally
occurring hormone in the body. Each are known for his
or her capability to increase muscle mass and strength, but they work in numerous ways and have completely different potential unwanted effects.
Both Anavar and Dianabol are potent anabolic steroids, and mixing them
can enhance the danger of unwanted effects and put a major pressure on the body.
Most notably, there’s a danger of liver problems, including liver tumors
and cysts. It’s all the time critical to consider the pros and
cons before considering taking this synthetic steroid, understanding and acknowledging the
dangers coming with the obvious advantages. Whereas Anavar may have its potential makes
use of, careful consideration and consultation should be a
prime priority. This information will stroll you
through everything you have to know about Anavar, from its makes use of to the potential side effects.
Whether Or Not you’re contemplating using anabolic steroids for medical
causes or health objectives, being knowledgeable may help you make
better selections. Anavar (oxandrolone) is a popular anabolic steroid
used by many individuals for different reasons.
Whereas it’s usually praised for its muscle-building
benefits, knowing how it works may help folks avoid the risks concerned
with its use.
Girls can anticipate wonderful outcomes from an Anavar cycle, including beautiful
strength features. You’ll be lifting heavier weights and will find your lifting motion improves with that power boost.
It’s probably the most tolerable and the least prone
to trigger virilizing signs at low to average doses.
For girls first treading into the world of AAS, Anavar is type of always the FIRST selection – and often the only alternative for these wanting to
avoid virilization. The lack of threat of water retention is a serious benefit
of Anavar and a huge purpose why it’s such a
popular and potent chopping compound, including
for aggressive customers.
Nonetheless, it is necessary to observe that everyone’s body reacts in a different way to
steroids, and a few individuals should still experience water retention while utilizing Anavar
– as I pointed out to start with. It is important to pay attention to these potential unwanted
facet effects and to speak together with your doctor should you experience any signs whereas taking Anavar.
With correct monitoring and administration, it is potential to safely use Anavar to realize your fitness goals.
This means you will not only experience elevated GFR and Creatinine levels, however additionally, you will expertise
elevated ALT and AST levels. All of these will
enhance the likeness of your body holding onto the
salt, that means you ought to have an increased chance of holding onto water as well.
Then contemplate the chopping stack if you’re seeking to
combine Anvarol with other related great slicing dietary supplements.
This could cause the blood strain to rise to harmful ranges, placing the person at risk for a heart attack or
stroke.
These are powerful authorized steroids that will allow you to construct
muscle, reduce fat, increase strength ranges, and
enhance endurance to make sure your workouts
can last more than ever earlier than. For athletes we assist
who’re experiencing elevated ALT/AST levels, TUDCA, a substance identified
to scale back liver pressure, has proved effective. Furthermore,
it’s highly cautioned in opposition to combining Winstrol with different oral steroids
to keep away from extreme liver injury. Measuring
fats loss with scales may be misleading as a result of simultaneous muscle growth.
Therefore, customers might see a decrease in physique fats when wanting
within the mirror, but the scales could present a rise as a substitute of a lower
when on either steroid. We strongly advise bodybuilders to keep away from using
trenbolone due to the doubtlessly fatal results it can cause.
If you’re serious about taking Anavar, or some other steroid for that matter, be certain to do your analysis first and consult with a certified medical professional.
Nonetheless, this stack will likely result in raised LDL
ldl cholesterol and liver enzymes. Not just this, it might also end in testosterone suppression because of Dianabol.
The added benefit is that Anavar can help reduce the bloating and puffiness that
come along with Dianabol due to water retention. Anavar is an oral steroid that’s alleged to be fairly delicate by way of side
effects. Trenbolone, then again, is a highly toxic injectable steroid.
ACut is the top-rated authorized Anavar alternative that mimics all the benefits of Anavar without any
of its unfavorable unwanted aspect effects.
Typically guys will introduce it into a stack about 4 weeks earlier than a contest
so as to dry them out to achieve that tremendous exhausting look.
Nevertheless, it often causes virilization unwanted side effects, inflicting girls to look and
sound more masculine. However, injecting steroids is not
a pleasing prospect for many people, Besides,
there are a high incidence of infections with Winstrol injections.
Winstrol is not appropriate for newbies due to
the severity of unwanted side effects that are sometimes experienced.
Winstrol dosages for men are sometimes 50 mg per day but can go as excessive as double that.
Anavar and Anadrol are both anabolic steroids that can be utilized for chopping.
Nonetheless, they have different properties, and so they is
probably not appropriate for everyone. Nevertheless, it’s important to notice that Anadrol also comes with
a excessive threat of unwanted aspect effects, significantly these associated to liver toxicity.
As A Result Of of this, it’s typically used for brief durations and underneath the supervision of a
healthcare skilled. Anadrol, also called Oxymetholone, is an oral anabolic steroid that belongs to the category of synthetic testosterone derivatives.
Nonetheless, many women barely notice any unfavorable
effects from such dosages. We have had success in accelerating the recovery of women’s endogenous testosterone when supplementing with DHEA, the official prescription treatment for girls with low androgen levels.
Nevertheless, we have had female sufferers whose voices have
deepened, their clitorises enlarged, or their menstrual cycles disrupted (when taking very high dosages or excessively long cycles).
We find that girls are hardly ever troubled by the unwanted
side effects of Anavar, especially from a masculinization/virilization perspective.
This reduction in visceral fats mass is particularly helpful for ladies, as they’re extra susceptible to storing belly fats.
This is due to the truth that they have
developed a tolerance to the drug and require a higher dose to
expertise effects. Twelve to sixteen weeks might be more suitable
for more seasoned customers. You can do that to get essentially
the most advantages attainable with out getting
any unfavorable unwanted effects.
This ester isn’t available as a person product but
only consumed in formulas like Sustanon and different mixed testosterone ester preparations.
Good post, and that is an example of a way of using steroids that i personally like, agree with and
suggest in some sure conditions. I havent tried Var, however have used winny 2 or three instances – each injected and orally,
i can quite actually say i have never noticed any effect from
it within the slightest. I might get my arms on winny if I actually needed to, I have almost
no entry to anavar I would belief to not be fake or underdosed, its
rare to me atleast. You can train for longer hours within the fitness center without
getting too exhausted. It is important to take into account all the information presented here.
Fortuitously, there are alternatives to Anavar and Winstrol that could be safer
and more cost-effective for these looking
for them.
Winstrol may cause abdomen upset and different digestive issues
if taken on an empty abdomen. It is recommended to take Winstrol with meals to attenuate the chance of these unwanted effects.
If you’re contemplating utilizing both of these supplements, it is important to speak
to a healthcare skilled first. They can help you establish which one is
right for you based in your particular person wants and goals.
The beneficial Clenbuterol and T3 cycle is often 6 weeks on and
6 weeks off, while the recommended Clenbuterol
and Winstrol cycle is usually 4-6 weeks.
If you use each collectively, the great effects would
possibly cancel one another out, and the bad results can worsen. Furthermore, Dianabol escalates erythrocyte depend, guaranteeing a copious
oxygen deluge for muscles, amplifying stamina and curtailing weariness.
Sure, LDL was significantly elevated in comparison with placebo remedy at forty and 80
mg, but not at 20 mg. There you will discover in the upper
proper of the screen a hyperlink to the free full text article.
Winstrol, or Stanozolol, is robust in phrases of muscle building however not as much as bulk-up steroids like Anadrol.
It also comes in tablet kind, which is great for many who don’t like photographs.
Our observations point out that Winstrol is more practical at building lean muscle tissue and facilitating fat
loss compared to Anavar. Theoretically, Anavar ought to show extra important
physique composition modifications with its anabolic score of
630 towards Winstrol’s 320. Trenbolone has by no means been approved for human consumption as a
outcome of its poisonous nature, and therefore, users are risking their short- and long-term health when taking this compound.
In our experience, combining trenbolone with other anabolic steroids in a stack
has resulted in additional well being deterioration. Trenbolone is essentially an injectable steroid utilized by bodybuilders to realize large
quantities of lean muscle and strength while enhancing
fats loss (1).
This strategy fosters the event of a lean, sculpted
physique by selling fat loss whereas maintaining muscle mass.
Pairing this routine with a balanced, protein-rich diet and common cardio and energy coaching further enhances outcomes.
In terms of fitness and bodybuilding objectives,
many women seek for an environment friendly and effective approach to obtain desired results.
Anavar, a preferred anabolic steroid, has
gained a reputation for providing a sturdy answer tailor-made particularly for the
female physique. It provides quite a few advantages, such as lean muscle
improvement, energy enhancement, and fats discount, making it a
gorgeous option for these keen on sculpting their dream body.
Girls in search of to maintain female traits have very limited
choices in phrases of steroid use. The described steroid chopping cycle for ladies is usually adopted by
female bikini fashions and bodybuilders aiming to reduce physique
fat. While some women choose to decrease their dosage progressively as they approach the end of the cycle, this step is not
obligatory. In cases the place women do decide to use
Winstrol steroid, we advocate a divided intake of two tablets per day somewhat
than a single dose.
The latter may be very fascinating since Oxandrolone is an oral steroid, most of which are onerous on the liver.
Some potential Anavar unwanted effects that you should be conscious of are gentle suppression, zits, hair loss and nausea.
HGH can present that extra push-through; the results will converse for themselves.
Intermediate users can improve the HGH dose to 6iu daily, with Trenbolone Enanthate and Testosterone
Cypionate at 400mg weekly. These are each long-lasting steroids, which makes them best for an extended cycle.
Like HGH, Trenbolone also will increase IGF-1, making this
mix an ideal match for mass-gaining and fat-loss objectives.
However, don’t expect var to have quite the fat-burning qualities
of clenbuterol or ephedrine. When it involves Anavar only cycle for males, the first objective
often revolves around chopping seasons, when the objective is to protect lean muscle tissue while shedding physique fat.
Although it isn’t sometimes used for massive positive aspects, it could present reasonable development in muscle mass, particularly for individuals who mix
the cycle with a well-planned food regimen and exercise routine.
The cycle usually lasts 6 to 8 weeks, with a day by day dosage ranging between 30 and 80mg.
Thus women should order a testing kit earlier than they take anavar, or any similar controlled substance.
Due to an increase in exogenous testosterone, women can turn into hornier on Anavar, with an elevated desire
for sex. Even if a woman did expertise such symptoms, they might be reversed after they came off Anavar.
Nevertheless, this doesn’t apply to the voice; which is a permanent impact
(5). In which case, if ladies did begin to notice decreased breast size (for example), they might lower their dose to forestall further virilization. 2
years later G.D Searle & Co introduced it to market, later underneath the brand name of ‘Anavar’,
with it successfully healing sufferers, by reversing their muscle-wasting situations.
The FDA was happy with its safety, approving it for human use, which stays the case
right now.
Steadily truly fizzling out the dosages and incorporating PCT medicines can help in the restoration process and preserve the positive
aspects made during the cycle. When organising a cycle stack with Winstrol and Anavar, it’s important to discover out the optimum dosage primarily
based in your objectives and previous experience with these compounds.
I’ve found that a balanced stack can result in impressive results whereas minimizing unwanted effects.
When it comes to an Anavar cycle, the outcomes can vary tremendously based mostly on multiple components.
Cautious planning helps form up the proper regimen to fulfill your
health goals. Whether you are aiming for muscle definition, a leaner physique,
boosted power, or even weight reduction, Oxandrolone’s
low androgenic properties make it less excessive than other steroids but effective.
Due to the potential risk of virilization effects, it’s advisable for females to adhere to
conservative dosing guidelines, with a maximum of 10 mg every day for cycles lasting not extra
than four to six weeks. Many women, notably health
models, attain stunningly sculpted and outlined physiques with simply
5-10 mg every day. Anavar or Oxandrolone is an oral anabolic-androgenic
steroid that’s used to advertise lean muscle mass and
was created in 1964.
Anavar, scientifically generally known as Oxandrolone,
is an oral anabolic steroid that is highly regarded for its potential
to advertise lean muscle gains, enhance energy, and enhance athletic performance.
On the other hand, TRT involves the administration of exogenous
testosterone to revive hormone levels in individuals with low testosterone.
Anavar, which is also identified by its drug name, Oxandrolone, or just “var,” is an anabolic steroid that’s turn out to be wildly in style amongst bodybuilders.
Clenbuterol can preserve present muscle while you’re on a calorie-restricted diet.
By nutrient partitioning, Clen can forestall fats
from being stored, encourage the use of fats for vitality, and
forestall the utilization of lean muscle. Nevertheless,
bodybuilders shouldn’t be complacent concerning the potential negative results of Anavar.
This is particularly true considering how incessantly it’s counterfeited and substituted for methandrostenolone on the black market (Dianabol).
The effects of Anavar on the female body will be considerably stronger,
even at considerably lower doses, than these utilized by men to get the
same outcomes.
The optimum day by day dosage of Anavar varies
depending on several factors, corresponding to your gender, body weight, expertise with steroids, and desired outcomes.
In terms of physique composition, on Winstrol, users’ muscle tissue are likely to look a
little deflated, due to a lack of intracellular water.
On Anavar, users’ muscular tissues are going to be very pumped, as a outcome of an increase of fluid volume inside the muscle cell.
Nonetheless, because of Winstrol’s superior muscle-building attributes, this distinction in glycogen storage is in all probability not noticeable.
Adjusting training and vitamin to enhance Anavar use is crucial for maximizing its benefits.
Many girls find they will practice with greater depth and frequency whereas on Anavar because
of its recovery-enhancing properties. Nevertheless, it’s essential to not
overdo it, as this could improve the risk of damage or burnout.
Nutrition must be tailor-made to help objectives, typically involving a high-protein food regimen with sufficient wholesome fats and sophisticated carbohydrates.
For those utilizing Anavar for chopping, a reasonable calorie deficit can be implemented to advertise fat loss while the compound helps protect muscle mass.
One of the primary causes Anavar is so valued in feminine bodybuilding is its ability to
promote lean muscle growth with out extreme bulk.
El uso de AAS es, de hecho, una de las formas más rápidas de
adquirir músculo y, como consecuencia, los culturistas
y atletas suelen tomar AAS, que desean volverse más grandes y
fuertes lo más rápido posible. La fisioterapia se presenta
como una alternativa al uso del ibuprofeno en el manejo del dolor crónico y la mejora
de las molestias asociadas a problemas de movilidad y postura.
Los fisioterapeutas utilizan una variedad de técnicas, que
incluyen ejercicios de fortalecimiento, estiramientos, manipulación y movilización de tejidos blandos, para alcanzar el objetivo.
Se utiliza como complemento en el tratamiento de diversas condiciones, incluyendo artritis, lesiones deportivas y dolor posoperatorio.
Tiene algunas propiedades antiinflamatorias y analgésicas cuando se consume
como suplemento, lo que puede aliviar el dolor asociado con la artrosis y mejorar
la movilidad en las articulaciones afectadas.
La dosis recomendada para adultos es de 500 a 1000 mg cada 6 horas,
sin exceder los four gramos al día. Si toma esteroides con regularidad, corre un mayor riesgo de contraer
infecciones.
Winstrol sobrevivió un poco en las décadas de 1980 y 1990,
cuando las compañías farmacéuticas dejaron de fabricar
varios esteroides anabólicos. La eficacia de la combinación de mesalazina y corticoides tópicos ha sido poco evaluada, por lo que se dispone de una evidencia científica muy limitada.
En un estudio holandés doble ciego se incluyeron 60 pacientes aleatorizados a
recibir tratamiento con enemas de beclometasona (3mg/100ml), enemas de mesalazina (2g/100ml) o la combinación de ambos durante 4 semanas.
Los corticoides pueden producir efectos secundarios, algunos de los cuales pueden causar problemas graves de salud.
Si conoces los efectos secundarios posibles, puedes tomar medidas para controlar su repercusión.
Si está buscando ganar músculo, fuerza y rendimiento, le sugiero que pruebe estos esteroides anabólicos legales.
Los esteroides legales pueden mejorar el progreso y el rendimiento de forma natural.
La dosis recomendada de Clenbutrol es tomar three cápsulas al
día con agua, unos forty five minutos antes del entrenamiento.
La dosis recomendada de Crazy Bulk Development
Stack es tomar three cápsulas al día con agua, unos forty five minutos antes del entrenamiento.
La dosis recomendada de Trenorol es tomar 3 cápsulas al día
con agua, unos 45 minutos antes del entrenamiento.
En cambio, funcionan de forma segura para ayudar a
mejorar la masa muscular, ayudar a la pérdida de peso y mejorar
la fuerza y la resistencia para los entrenamientos más extenuantes.
Los esteroides anabólicos han sido prohibidos para la construcción de músculo debido al daño que causan. Ahora sólo se permite su uso para el tratamiento de diversas afecciones, como
el retraso de la pubertad. Trembolona es un esteroide prohibido y Trenorol está destinado a replicar
todos sus beneficios sin ninguno de los efectos secundarios que vienen de usar el esteroide.
Además de ayudar a la pérdida de peso, este suplemento es
también grande para mantener la grasa corporal saludable a la proporción de músculo magro.
D-Bal es considerado como una de las mejores alternativas de esteroides por algunas
razones.
Los resultados primarios fueron la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud (CVRS) específica de la
enfermedad, la gravedad de la enfermedad informada por el
paciente y el evento adverso más común – epistaxis (hemorragia nasal).
Los resultados secundarios incluyeron la CVRS common, la puntuación endoscópica de
los pólipos nasales, la puntuación de la tomografía computadorizada (TC) y el evento adverso de la irritación local.
Se utilizó GRADE para evaluar la calidad de las pruebas para cada resultado; esto
se indica en cursiva. Esta revisión es una de seis que examinan las opciones
primarias de tratamiento médico para los pacientes con rinosinusitis crónica.
Recomendamos a los pacientes que consulten todas las opciones con su médico y obtengan una segunda opinión antes de tomar una decisión sobre el
tratamiento. Es un fluido que ayuda a lubricar las articulaciones
para protegerlas del desgaste. Las inyecciones o infiltraciones son otro método común utilizado
para reducir rápidamente la inflamación y el dolor de
rodilla.
También activaría fibras nerviosas específicas que envían señales al sistema nervioso
central. También se comercializa un polvo, que puede disolverse en agua y tomarse
una vez al día, con las comidas. El aceite de pescado es un suplemento dietético rico en ácidos grasos omega-3, especialmente ácido eicosapentaenoico (EPA) y ácido docosahexaenoico
(DHA).
Tenga en cuenta que debe seguir absolutamente la terapia post ciclo o PCT apropiada para contrarrestar los efectos secundarios
de las prohormonas. Por ejemplo, pruebe COMPLEX PCT, una terapia compleja
de ciclo publish altamente efectiva producida por Vitamin. Descubre los mejores esteroides legales para aumentar masa muscular de forma segura y efectiva.
Clenbutrol es eficaz para mantener una proporción saludable de músculo
magro a grasa, un efecto que se logra mediante el
uso de varios ingredientes termogénicos. Estos ingredientes termogénicos aumentan la temperatura interna
del cuerpo, lo que hace que el cuerpo aumente sus tasas metabólicas
para bajar su temperatura interna. Esta tasa rápida
del metabolismo es responsable de las propiedades de quema de grasa de Clenbutrol.
Estas mejoras conducen a que el sistema cardiovascular funcione
a niveles óptimos.
Este proceso se produce debido a cantidades excesivas de testosterona exógena
presente en el torrente sanguíneo, y por lo tanto el cuerpo trata de mantener la homeostasis.
Desafortunadamente, la testosterona no es el esteroide anabólico más conveniente para la administración, siendo predominantemente inyectable.
Sin embargo, este método de entrada significa que puede pasar por alto el hígado (a diferencia de los
esteroides alfa alquilados c-17), ingresando así al torrente
sanguíneo de inmediato. Los glicósidos cardíacos son esteroides compuestos por esqueletos cardanólidos, formados por 23 átomos de carbono y un anillo de
lactona como sustituyente en el carbono 17. A partir
de la estructura básica del esterano con cuatro anillos fusionados,
tres ciclohexanos nombrados con las letras A, B y C y un ciclopentano nombrado con la letra D, se forman cientos de estructuras esteroideas naturales y sintéticas.
En lugar de buscar esteroides poco confiables, no confiables e inseguros de los distribuidores del mercado negro, puede
obtener exactamente los auténticos esteroides que necesita
para ejecutar programas de corte y aumento de volumen. En medicina esteroide, hubo
un momento en el que se podían obtener esteroides anabólicos de
venta libre, luego regulaciones estrictas (Esteroides anabólicos Management Act de 1990) prohibió la
posesión y el uso de esteroides. Un estudio de 2014 encontró que los participantes que la usaron durante un período de
entrenamiento de 6 semanas reportaban mayor energía
y mejor concentración, pero no aumentaban su masa corporal ni su rendimiento common. Es una
sustancia pure que se encuentra en alimentos como el pescado y
la carne.
Estos esteroides son diferentes de los esteroides anabólicos, que son medicamentos que son químicamente similares a la
hormona masculina testosterona. El Dianabol fue un esteroide anabólico muy popular en los Estados Unidos, pero debido a
su fuerte composición química y a varios efectos secundarios negativos,
fue declarado como un producto inseguro y ahora está prohibido.
CrazyBulk ha credo D-Bal como la opción más segura y
legal para ofrecer todos los beneficios que ofrecía Dianabol, pero
sin los componentes peligrosos y los efectos secundarios que este genero en sus
consumidores.